Aziridination Reactivity of a Manganese(II) Complex with a Bulky Chelating Bis(Alkoxide) Ligand
- PMID: 36144492
- PMCID: PMC9505844
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27185751
Aziridination Reactivity of a Manganese(II) Complex with a Bulky Chelating Bis(Alkoxide) Ligand
Abstract
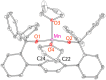
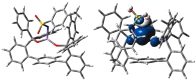
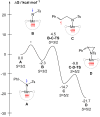
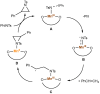
Treatment of Mn(N(SiMe3)2)2(THF)2 with bulky chelating bis(alkoxide) ligand [1,1':4',1''-terphenyl]-2,2''-diylbis(diphenylmethanol) (H2[O-terphenyl-O]Ph) formed a seesaw manganese(II) complex Mn[O-terphenyl-O]Ph(THF)2, characterized by structural, spectroscopic, magnetic, and analytical methods. The reactivity of Mn[O-terphenyl-O]Ph(THF)2 with various nitrene precursors was investigated. No reaction was observed between Mn[O-terphenyl-O]Ph(THF)2 and aryl azides. In contrast, the treatment of Mn[O-terphenyl-O]Ph(THF)2 with iminoiodinane PhINTs (Ts = p-toluenesulfonyl) was consistent with the formation of a metal-nitrene complex. In the presence of styrene, the reaction led to the formation of aziridine. Combining varying ratios of styrene and PhINTs in different solvents with 10 mol% of Mn[O-terphenyl-O]Ph(THF)2 at room temperature produced 2-phenylaziridine in up to a 79% yield. Exploration of the reactivity of Mn[O-terphenyl-O]Ph(THF)2 with various olefins revealed (1) moderate aziridination yields for p-substituted styrenes, irrespective of the electronic nature of the substituent; (2) moderate yield for 1,1'-disubstituted α-methylstyrene; (3) no aziridination for aliphatic α-olefins; (4) complex product mixtures for the β-substituted styrenes. DFT calculations suggest that iminoiodinane is oxidatively added upon binding to Mn, and the resulting formal imido intermediate has a high-spin Mn(III) center antiferromagnetically coupled to an imidyl radical. This imidyl radical reacts with styrene to form a sextet intermediate that readily reductively eliminates the formation of a sextet Mn(II) aziridine complex.
Keywords: alkoxides; aziridination; iminoiodinane; manganese.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Sweeney J.B. Aziridines: Epoxides’ Ugly Cousins? Chem. Soc. Rev. 2002;31:247–258. - PubMed
-
- Paike V.V., Kauthale S.S., Kumar R.C., Katariya M.V., More R.R., Ameta K.L., Mane S.B. Aziridines: Synthesis and bioactivity. In: Ameta K.L., Pawar R.P., Domb A.J., editors. Bioactive Heterocycles. Nova Scientific Publishers; Hauppauge, NY, USA: 2013. pp. 41–68.
-
- Kametani T., Honda T. Application of Aziridines to the Synthesis of Natural Products. Adv. Heterocycl. Chem. 1986;39:181–236.
-
- Werner L., Machara A., Sullivan B., Carrera I., Moser M., Adams D.R., Hudlicky T. Several Generations of Chemoenzymatic Synthesis of Oseltamivir (Tamiflu): Evolution of Strategy, Quest for a Process-Quality Synthesis, and Evaluation of Efficiency Metrics. J. Org. Chem. 2011;76:10050–10067. - PubMed
-
- Hanessian S., Guesne S., Chenard E. Total Synthesis of “Aliskiren”: The First Renin Inhibitor in Clinical Practice for Hypertension. Org. Lett. 2010;12:1816–1819. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

