A Comprehensive Review with Updated Future Perspectives on the Ethnomedicinal and Pharmacological Aspects of Moringa oleifera
- PMID: 36144493
- PMCID: PMC9504211
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27185765
A Comprehensive Review with Updated Future Perspectives on the Ethnomedicinal and Pharmacological Aspects of Moringa oleifera
Abstract
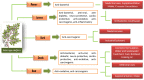
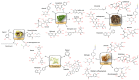
Moringa oleifera is an ancient remedy plant, known as the miraculous plant due to its many prominent uses and significant health benefits. It is a nutrient-rich plant, with exceptional bioactive compounds, such as polyphenols that possess several medicinal properties. Many significant studies have been carried out to evaluate the ethnomedicinal and pharmacological properties of M. oleifera in various applications. Therefore, this comprehensive review compiles and summarizes important findings from recent studies on the potential properties of different parts of M. oleifera. The pharmacological properties of M. oleifera have been studied for various potential biological properties, such as cardio-protective, anti-oxidative, antiviral, antibacterial, anti-diabetic and anti-carcinogenic effects. Therefore, the potential of this plant is even more anticipated. This review also highlights the safety and toxicity effects of M. oleifera treatment at various doses, including in vitro, in vivo and clinical trials from human studies.
Keywords: M. oleifera; antioxidant activity; bioactive compounds; nutritional composition; pharmacological properties; polyphenols.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Moringa oleifera: An Updated Comprehensive Review of Its Pharmacological Activities, Ethnomedicinal, Phytopharmaceutical Formulation, Clinical, Phytochemical, and Toxicological Aspects.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 20;24(3):2098. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032098. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768420 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacological, nutritional and antimicrobial uses of Moringa oleifera Lam. leaves in poultry nutrition: an updated knowledge.Poult Sci. 2022 Sep;101(9):102031. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2022.102031. Epub 2022 Jun 24. Poult Sci. 2022. PMID: 35926350 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Moringa oleifera: A Tree of Life as a Promising Medicinal Plant for Neurodegenerative Diseases.J Agric Food Chem. 2021 Dec 8;69(48):14358-14371. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.1c04581. Epub 2021 Nov 29. J Agric Food Chem. 2021. PMID: 34843254 Review.
-
Health benefits of Moringa oleifera.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014;15(20):8571-6. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2014.15.20.8571. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014. PMID: 25374169 Review.
-
Exploring the potential of Moringa oleifera Lam in skin disorders and cosmetics: nutritional analysis, phytochemistry, geographical distribution, ethnomedicinal uses, dermatological studies and cosmetic formulations.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 Jun;397(6):3635-3662. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02862-2. Epub 2023 Dec 6. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38055069 Review.
Cited by
-
Medicinal Plant Extracts against Cardiometabolic Risk Factors Associated with Obesity: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Targets.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Jul 21;17(7):967. doi: 10.3390/ph17070967. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39065815 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Moringa oleifera: A Review on the Antiproliferative Potential in Breast Cancer Cells.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 Aug 18;45(8):6880-6902. doi: 10.3390/cimb45080434. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37623253 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative Analysis of Moringa oleifera Lam. Leaves Ethanolic Extracts: Effects of Extraction Methods on Phytochemicals, Antioxidant, Antimicrobial, and In Ovo Profile.Plants (Basel). 2025 May 29;14(11):1653. doi: 10.3390/plants14111653. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40508327 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic tapestry of Capsicum fruit colors: a comparative analysis of four cultivated species.Theor Appl Genet. 2024 May 14;137(6):130. doi: 10.1007/s00122-024-04635-8. Theor Appl Genet. 2024. PMID: 38744692
-
Incorporation of Moringa oleifera Leaf Extract in Yoghurts to Mitigate Children's Malnutrition in Developing Countries.Molecules. 2023 Mar 9;28(6):2526. doi: 10.3390/molecules28062526. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36985498 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Luetragoon T., Sranujit R.P., Noysang C., Thongsri Y., Potup P., Suphrom N., Nuengchamnong N., Usuwanthim K. Bioactive Compounds in Moringa oleifera Lam. Leaves Inhibit the Pro-Inflammatory Mediators in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Human Monocyte-Derived Macrophages. Molecules. 2020;25:191. doi: 10.3390/molecules25010191. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Padayachee B., Baijnath H. An overview of the medicinal importance of Moringaceae. J. Med. Plants Res. 2012;6:5831–5839. doi: 10.5897/JMPR12.1187. - DOI
-
- Padayachee B., Baijnath H. An updated comprehensive review of the medicinal, phytochemical and pharmacological properties of Moringa oleifera. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2020;129:304–316. doi: 10.1016/j.sajb.2019.08.021. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

