Identification of Coumarins and Antimicrobial Potential of Ethanolic Extracts of Dipteryx odorata and Dipteryx punctata
- PMID: 36144574
- PMCID: PMC9505109
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27185837
Identification of Coumarins and Antimicrobial Potential of Ethanolic Extracts of Dipteryx odorata and Dipteryx punctata
Abstract
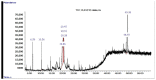
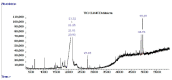
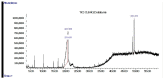
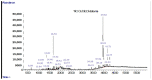
Dipteryx odorata and Dipteryx punctata are species native to the Amazonian, traded by extractivists to obtain coumarin. We aimed to analyze the presence of coumarin in the ethanolic extracts of leaves, branches and fruits of D. odorata and D. punctata and to evaluate the antimicrobial activity of these extracts against phytopathogenic fungi and bacteria of clinical interest. Chemical analyses were performed by thin layer chromatography (TLC) and by gas chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry (GC-MS). For the antifungal assays, the fungi used were Cercospora longissima, Colletotrichum gloeosporioides, two isolates of Fusarium spp. and Sclerotium rolfsii, and the antibacterial assay was performed using the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) test with Burkholderia cepacia, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus bacteria. In D. odorata seed extracts and in D. punctata husks, endocarps, and seeds, we identified 1,2-benzopyrone. D. odorata endocarp extracts and D. punctata seeds provided the greatest decrease in mycelial growth of the evaluated phytopathogens, showing promise as an alternative control. The husk and endocarp extracts of both species had a weak effect on E. coli. This research is the first to compare the different parts of species of the genus Dipteryx and to evaluate the use of husks and endocarps of D. punctata fruits to obtain coumarin. Chemical analyses used to quantify the compounds existing in the extracts, and tests with phytopathogens in vitro and in vivo are currently being carried out.
Keywords: antimicrobial activity; chromatography; cumaru extracts; natural products.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




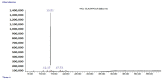
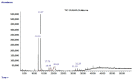
References
-
- The Plant List: A Working List of All Plant Species. 2010. [(accessed on 20 January 2021)]. Available online: http://www.theplantlist.org.
-
- Barata L.E.S. Empirismo e ciência: Fonte de novos fitomedicamentos. Cienc. Cult. 2005;57:4–5.
-
- Fernandes O.C.C., Carneiro A.L.B., Silva A.B., Feitosa K.B., Lemos R.A., Filho R.F.C., Silva J.C. Compostos Naturais e Atividade Antimicrobiana. In: Teixeira M.F.S., Silva T.A., Palheta R.A., Carneiro A.L.B., Atayde H.M., editors. Fungos da Amazônia: Uma Riqueza Inexplorada (Aplicações Biotecnológicas) da Universidade Federal do Amazonas; Manaus, Brazil: 2011. pp. 82–103.
-
- Ourhzif E., Ricelli A., Stagni V., Cirigliano A., Rinaldi T., Bouissane L., Saso L., Chalard P., Troin Y., Khouili M., et al. Antifungal and Cytotoxic Activity of Diterpenes and Bisnorsesquiterpenoides from the Latex of Euphorbia resinifera Berg. Molecules. 2022;27:5234. doi: 10.3390/molecules27165234. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

