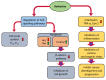
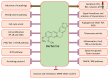
Berberine: An Important Emphasis on Its Anticancer Effects through Modulation of Various Cell Signaling Pathways
- PMID: 36144625
- PMCID: PMC9505063
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27185889
Berberine: An Important Emphasis on Its Anticancer Effects through Modulation of Various Cell Signaling Pathways
Abstract
Cancer is the most commonly diagnosed type of disease and a major cause of death worldwide. Despite advancement in various treatment modules, there has been little improvement in survival rates and side effects associated with this disease. Medicinal plants or their bioactive compounds have been extensively studied for their anticancer potential. Novel drugs based on natural products are urgently needed to manage cancer through attenuation of different cell signaling pathways. In this regard, berberine is a bioactive alkaloid that is found in variety of plants, and an inverse association has been revealed between its consumption and cancer. Berberine exhibits an anticancer role through scavenging free radicals, induction of apoptosis, cell cycle arrest, inhibition of angiogenesis, inflammation, PI3K/AKT/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), Wnt/β-catenin, and the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway. In addition, synergistic effects of berberine with anticancer drugs or natural compounds have been proven in several cancers. This review outlines the anticancer effects and mechanisms of action of berberine in different cancers through modulation of various cell signaling pathways. Moreover, the recent developments in the drug delivery systems and synergistic effect of berberine are explained.
Keywords: berberine; bioavailability; cancer; cell signaling pathways; synergistic effects.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest for this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Berberine represses human gastric cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo by inducing cytostatic autophagy via inhibition of MAPK/mTOR/p70S6K and Akt signaling pathways.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Aug;128:110245. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110245. Epub 2020 May 23. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32454290
-
Peruvoside targets apoptosis and autophagy through MAPK Wnt/β-catenin and PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathways in human cancers.Life Sci. 2020 Jan 15;241:117147. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.117147. Epub 2019 Dec 9. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 31830480
-
Combination treatment of berberine and solid lipid curcumin particles increased cell death and inhibited PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway of human cultured glioblastoma cells more effectively than did individual treatments.PLoS One. 2019 Dec 16;14(12):e0225660. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0225660. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31841506 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory Potential of Dietary Nutraceuticals on Cellular PI3K/Akt Signaling: Implications in Cancer Prevention and Therapy.Curr Top Med Chem. 2021;21(20):1816-1831. doi: 10.2174/1568026621666210716152224. Curr Top Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34279200 Review.
-
Natural products targeting autophagy via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway as anticancer agents.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2013 Sep;13(7):1048-56. doi: 10.2174/18715206113139990130. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 23293890 Review.
Cited by
-
Coptis rhizome extract influence on Streptococcus pneumoniae through autolysin activation.AMB Express. 2024 Jul 4;14(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s13568-024-01736-x. AMB Express. 2024. PMID: 38965154 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in Metabolite Profiles of Dihydroberberine and Micellar Berberine in Caco-2 Cells and Humans-A Pilot Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 22;25(11):5625. doi: 10.3390/ijms25115625. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38891813 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Berberine-Loaded Nanoparticles for Astrocytoma Cells Administration and Photodynamic Therapy Stimulation.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Mar 27;15(4):1078. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15041078. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37111564 Free PMC article.
-
Myricetin: A Significant Emphasis on Its Anticancer Potential via the Modulation of Inflammation and Signal Transduction Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 2;24(11):9665. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119665. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37298616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antioxidant and Cytotoxic Properties of Berberis vulgaris (L.) Stem Bark Dry Extract.Molecules. 2024 Apr 29;29(9):2053. doi: 10.3390/molecules29092053. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38731544 Free PMC article.
References
-
- IARC . In: World Cancer Report, 2008. Boyle P., Levin B.E., editors. IARC Press; Lyon, France: 2008.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous