α-Linolenic Acid Screened by Molecular Docking Attenuates Inflammation by Regulating Th1/Th2 Imbalance in Ovalbumin-Induced Mice of Allergic Rhinitis
- PMID: 36144628
- PMCID: PMC9501164
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27185893
α-Linolenic Acid Screened by Molecular Docking Attenuates Inflammation by Regulating Th1/Th2 Imbalance in Ovalbumin-Induced Mice of Allergic Rhinitis
Abstract
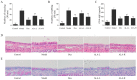
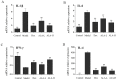
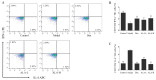
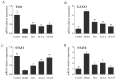
α-Linolenic acid (ALA) is a natural essential fatty acid widely found in plant seed oils and beans, which shows positive anti-inflammatory and antiallergic effects. In our previous study, ALA was proven to bind tightly to the seven protein targets closely associated with allergic rhinitis (AR) by molecular docking, which indicates that ALA may have a potential role in the treatment of AR. A mouse model of AR induced by ovalbumin (OVA) was adopted in this study to explore the therapeutical effect and potential mechanism of ALA in treating AR. Results demonstrated that ALA remarkably relieved the nasal symptoms, reduced the OVA-sIgE level in the serum, relieved the histopathological injuries, and downregulated the mRNA expression levels of IL-6 and IL-1β in the nasal mucosa. ALA also remarkably moderated the imbalance of Th1/Th2 cells, increased the mRNA expression levels of T-bet and STAT1, and reduced GATA3 and STAT6. ALA was proven to have a substantial therapeutic effect on mice with AR, and the underlying mechanism was likely to be the regulation of Th1/Th2 imbalance through the JAK/T-bet/STAT1 and JAK/GATA3/STAT6 pathways. This study provides a specific experimental basis for the clinical use and drug development of ALA in the treatment of AR.
Keywords: Th1/Th2 imbalance; allergic rhinitis; molecular docking; mouse model; α-Linolenic acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Yang L.Z., Yu B.L. New progress in the treatment of allergic rhinitis. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2013;21:543–546.
-
- Shark A.H., Crawford M.A., Reifen R. Update on alpha-linelic acid. Nutr. Rev. 2008;66:326–332. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

