Heterologous Expression and Catalytic Properties of Codon-Optimized Small-Sized Bromelain from MD2 Pineapple
- PMID: 36144767
- PMCID: PMC9502857
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27186031
Heterologous Expression and Catalytic Properties of Codon-Optimized Small-Sized Bromelain from MD2 Pineapple
Abstract
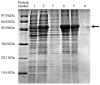
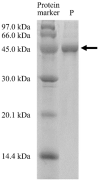
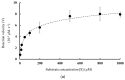
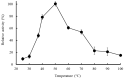
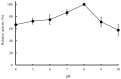
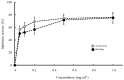
Bromelain is a unique enzyme-based bioactive complex containing a mixture of cysteine proteases specifically found in the stems and fruits of pineapple (Ananas comosus) with a wide range of applications. MD2 pineapple harbors a gene encoding a small bromelain cysteine protease with the size of about 19 kDa, which might possess unique properties compared to the other cysteine protease bromelain. This study aims to determine the expressibility and catalytic properties of small-sized (19 kDa) bromelain from MD2 pineapple (MD2-SBro). Accordingly, the gene encoding MD2-SBro was firstly optimized in its codon profile, synthesized, and inserted into the pGS-21a vector. The insolubly expressed MD2-SBro was then resolubilized and refolded using urea treatment, followed by purification by glutathione S-transferase (GST) affinity chromatography, yielding 14 mg of pure MD2-SBro from 1 L of culture. The specific activity and catalytic efficiency (kcat/Km) of MD2-SBro were 3.56 ± 0.08 U mg-1 and 4.75 ± 0.23 × 10-3 µM-1 s-1, respectively, where optimally active at 50 °C and pH 8.0, and modulated by divalent ions. The MD2-SBro also exhibited the ability to scavenge the 2,2-diphenyl-1-picryl-hydrazyl-hydrate (DPPH) with an IC50 of 0.022 mg mL-1. Altogether, this study provides the production feasibility of active and functional MD2-Bro as a bioactive compound.
Keywords: antioxidant; bromelain; catalytic activity; expression; metal ion; purification.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Soluble Expression and Catalytic Properties of Codon-Optimized Recombinant Bromelain from MD2 Pineapple in Escherichia coli.Protein J. 2021 Jun;40(3):406-418. doi: 10.1007/s10930-021-09974-9. Epub 2021 Mar 13. Protein J. 2021. PMID: 33713245
-
The proteolytic system of pineapple stems revisited: Purification and characterization of multiple catalytically active forms.Phytochemistry. 2017 Jun;138:29-51. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2017.02.019. Epub 2017 Feb 23. Phytochemistry. 2017. PMID: 28238440
-
Stability, purification, and applications of bromelain: A review.Biotechnol Prog. 2016 Jan-Feb;32(1):5-13. doi: 10.1002/btpr.2190. Epub 2015 Nov 17. Biotechnol Prog. 2016. PMID: 26518672 Review.
-
Comparative structural analysis of fruit and stem bromelain from Ananas comosus.Food Chem. 2018 Nov 15;266:183-191. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.05.125. Epub 2018 May 30. Food Chem. 2018. PMID: 30381175
-
Anticancer Potential of Pineapple and its Bioactive Compound Bromelain.Curr Pharm Des. 2025;31(6):461-483. doi: 10.2174/0113816128303910240713180835. Curr Pharm Des. 2025. PMID: 39279108 Review.
Cited by
-
Enhancing Bromelain Recovery from Pineapple By-Products: A Sustainable Approach for Value Addition and Waste Reduction.Foods. 2024 Feb 15;13(4):589. doi: 10.3390/foods13040589. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38397568 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of plant growth regulators DA-6 and COS on drought tolerance of pineapple through bromelain and oxidative stress.BMC Plant Biol. 2023 Apr 5;23(1):180. doi: 10.1186/s12870-023-04200-3. BMC Plant Biol. 2023. PMID: 37020215 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Therapeutic Potential of Bromelain: Applications, Benefits, and Mechanisms.Nutrients. 2024 Jun 28;16(13):2060. doi: 10.3390/nu16132060. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38999808 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ketnawa S., Chaiwut P., Rawdkuen S. Pineapple wastes: A potential source for bromelain extraction. Food Bioprod. Process. 2012;90:385–391. doi: 10.1016/j.fbp.2011.12.006. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

