Production of Salvianic Acid A from l-DOPA via Biocatalytic Cascade Reactions
- PMID: 36144828
- PMCID: PMC9501478
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27186088
Production of Salvianic Acid A from l-DOPA via Biocatalytic Cascade Reactions
Abstract
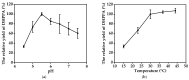
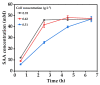
Salvianic acid A (SAA), as the main bioactive component of the traditional Chinese herb Salvia miltiorrhiza, has important application value in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. In this study, a two-step bioprocess for the preparation of SAA from l-DOPA was developed. In the first step, l-DOPA was transformed to 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (DHPPA) using engineered Escherichia coli cells expressing membrane-bound L-amino acid deaminase from Proteus vulgaris. After that, the unpurified DHPPA was directly converted into SAA by permeabilized recombinant E. coli cells co-expressing d-lactate dehydrogenase from Pediococcus acidilactici and formate dehydrogenase from Mycobacterium vaccae N10. Under optimized conditions, 48.3 mM of SAA could be prepared from 50 mM of l-DOPA, with a yield of 96.6%. Therefore, the bioprocess developed here was not only environmentally friendly, but also exhibited excellent production efficiency and, thus, is promising for industrial SAA production.
Keywords: biocatalysis; biological engineering; l-DOPA; membrane-bound l-amino acid deaminases; molecular biology; salvianic acid A.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Zhao B.L., Jiang W., Zhao Y., Hou J.W., Xin W.J. Scavenging Effects of Salvia Miltiorrhiza on Free Radicals and Its Protection for Myocardial Mitochondrial Membranes from Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Int. 1996;38:1171–1182. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

