Helical versus Flat Bis-Ferrocenyl End-Capped Peptides: The Influence of the Molecular Skeleton on Redox Properties
- PMID: 36144860
- PMCID: PMC9503075
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27186128
Helical versus Flat Bis-Ferrocenyl End-Capped Peptides: The Influence of the Molecular Skeleton on Redox Properties
Abstract
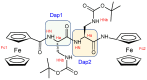
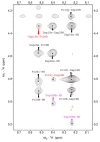
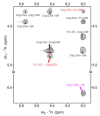
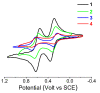
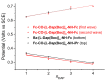
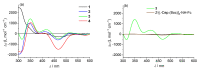
Despite the fact that peptide conjugates with a pendant ferrocenyl (Fc) have been widely investigated, bis-ferrocenyl end-capped peptides are rarely synthetized. In this paper, in addition to the full characterization of the Fc-CO-[L-Dap(Boc)]n-NH-Fc series, we report a comparison of the three series of bis-ferrocenyl homopeptides synthesized to date, to gain insights into the influence of α-amino isobutyric (Aib), 2,3-diamino propionic (Dap) and Cα,β-didehydroalanine (ΔAla) amino acids on the peptide secondary structure and on the ferrocene redox properties. The results obtained by 2D NMR analysis and X-ray crystal structures, and further supported by electrochemical data, evidence different behaviors depending on the nature of the amino acid; that is, the formation of 310-helices or fully extended (2.05-helix) structures. In these foldamers, the orientation of the carbonyl groups in the peptide helix yields a macrodipole with the positive pole on the N-terminal amino acid and the negative pole on the C-terminal amino acid, so that oxidation of the Fc moieties takes place more or less easily depending on the orientation of the macrodipole moment as the peptide chain grows. Conversely, the fully extended conformation adopted by ΔAla flat peptides neither generates a macrodipole nor affects Fc oxidation. The utilization as electrochemical and optical (Circular Dichroism) probes of the two terminal Fc groups, bound to the same peptide chain, makes it possible to study the end-to-end effects of the positive charges produced by single and double oxidations, and to evidence the presence "exciton-coupled" CD among the two intramolecularly interacting Fc groups of the L-Dap(Boc) series.
Keywords: 2,3-diamino propionic acid; Cα,β-didehydroalanine; electrochemistry; exciton-coupled Circular Dichroism; ferrocene; helical peptides; macrodipole; α-amino isobutyric acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
New bis-ferrocenyl end-capped peptides: synthesis and charge transfer properties.Biopolymers. 2013;100(1):14-24. doi: 10.1002/bip.22197. Biopolymers. 2013. PMID: 23335164
-
Chiral ferrocene amines derived from amino acids and peptides: synthesis, solution and X-ray crystal structures and electrochemical investigations.Inorg Chem. 2000 Nov 27;39(24):5437-43. doi: 10.1021/ic000089+. Inorg Chem. 2000. PMID: 11154558
-
Incorporation of Putative Helix-Breaking Amino Acids in the Design of Novel Stapled Peptides: Exploring Biophysical and Cellular Permeability Properties.Molecules. 2019 Jun 20;24(12):2292. doi: 10.3390/molecules24122292. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31226791 Free PMC article.
-
Ferrocenoyl amino acids and peptides: probing peptide structure.Met Ions Biol Syst. 2001;38:385-409. Met Ions Biol Syst. 2001. PMID: 11219016 Review.
-
The world of beta- and gamma-peptides comprised of homologated proteinogenic amino acids and other components.Chem Biodivers. 2004 Aug;1(8):1111-239. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.200490087. Chem Biodivers. 2004. PMID: 17191902 Review.
References
-
- Moriuchi T. Helical Chirality of Ferrocene Moieties in Cyclic Ferrocene-Peptide Conjugates. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2022;2022:e202100. doi: 10.1002/ejic.202100902. - DOI
-
- Qin Y., Tong F., Zhang W., Zhou Y., He S.Q., Xie R., Lei T., Wang Y.S., Peng S.J., Li Z.F., et al. Self-Delivered Supramolecular Nanomedicine with Transformable Shape for Ferrocene-Amplified Photodynamic Therapy of Breast Cancer and Bone Metastases. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021;31:2104645. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202104645. - DOI
-
- Gómez J., Sierra D., Ojeda C., Thavalingam S., Miller R., Guzmán F., Metzler-Nolte N. Solid-phase synthesis and evaluation of linear and cyclic ferrocenoyl/ruthenocenoyl water-soluble hexapeptides as potential antibacterial compounds. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2021;26:599–615. doi: 10.1007/s00775-021-01877-5. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

