One-Step Preparation of PVDF/GO Electrospun Nanofibrous Membrane for High-Efficient Adsorption of Cr(VI)
- PMID: 36144902
- PMCID: PMC9503595
- DOI: 10.3390/nano12183115
One-Step Preparation of PVDF/GO Electrospun Nanofibrous Membrane for High-Efficient Adsorption of Cr(VI)
Abstract
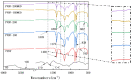
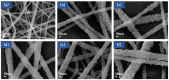
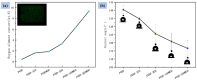
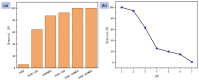
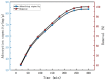
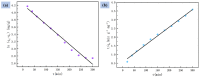
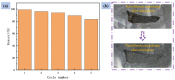
Mass loading of functional particles on the surface of nanofibers is the key to efficient heavy metal treatment. However, it is still difficult to prepare nanofibers with a large number of functional particle loads on the surface simply and efficiently, which hinders the further improvement of performance and increases the cost. Here, a new one-step strategy was developed to maximize the adhesion of graphene oxide (GO) particle to the surface of polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) nanofibers, which was combined with coaxial surface modification technology and blended electrospinning. The oxygen content on the as-prepared fiber surface increased from 0.44% to 9.32%, showing the maximized GO load. The increased adsorption sites and improved hydrophilicity greatly promoted the adsorption effect of Cr(VI). The adsorption capacity for Cr(VI) was 271 mg/g, and 99% removal rate could be achieved within 2 h for 20 mL Cr(VI) (100 mg/L), which was highly efficient. After five adsorption-desorption tests, the adsorption removal efficiency of the Cr(VI) maintained more than 80%, exhibiting excellent recycling performance. This simple method achieved maximum loading of functional particles on the fiber surface, realizing the efficient adsorption of heavy metal ions, which may promote the development of heavy-metal-polluted water treatment.
Keywords: Cr(VI) adsorption; coaxial electrospinning; graphene oxide; heavy metal wastewater treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Superhydrophilic Quaternized Electrospun Nanofibers for Fast and Efficient Removal of Cr(VI) from Metallurgical Wastewater.Langmuir. 2025 Jun 10;41(22):14533-14547. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.5c01799. Epub 2025 May 28. Langmuir. 2025. PMID: 40434892
-
Blend-electrospun graphene oxide/Poly(vinylidene fluoride) nanofibrous membranes with high flux, tetracycline removal and anti-fouling properties.Chemosphere. 2018 Sep;207:347-356. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.05.096. Epub 2018 May 17. Chemosphere. 2018. PMID: 29803884
-
Highly efficient removal of Cr(VI) from water based on graphene oxide incorporated flower-like MoS2 nanocomposite prepared in situ hydrothermal synthesis.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020 Apr;27(12):13882-13894. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-07978-z. Epub 2020 Feb 8. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32036519
-
A Review on Heavy Metal Ions and Containing Dyes Removal Through Graphene Oxide-Based Adsorption Strategies for Textile Wastewater Treatment.Chem Rec. 2021 Jul;21(7):1570-1610. doi: 10.1002/tcr.202000153. Epub 2021 Feb 4. Chem Rec. 2021. PMID: 33539046 Review.
-
A critical review on the electrospun nanofibrous membranes for the adsorption of heavy metals in water treatment.J Hazard Mater. 2021 Jan 5;401:123608. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123608. Epub 2020 Aug 15. J Hazard Mater. 2021. PMID: 33113718 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Progress on the Adsorption of Heavy Metal Ions Pb(II) and Cu(II) from Wastewater.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024 Jun 16;14(12):1037. doi: 10.3390/nano14121037. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38921913 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electrospun Zr-Doped CaO Sorbent for CO2 Capture.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023 Feb 16;13(4):747. doi: 10.3390/nano13040747. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36839115 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced Graphene Oxide/Waste-Derived TiO2 Composite Membranes: Preliminary Study of a New Material for Hybrid Wastewater Treatment.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023 Mar 14;13(6):1043. doi: 10.3390/nano13061043. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36985937 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang R.S., Liang R.H., Dai T.T., Chen J., Shuai X.X., Liu C. Pectin-based adsorbents for heavy metal ions: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019;91:319–329. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2019.07.033. - DOI
-
- Azimi A., Azari A., Rezakazemi M., Ansarpour M. Removal of Heavy Metals from Industrial Wastewaters: A Review. ChemBioEng Rev. 2017;4:37–59. doi: 10.1002/cben.201600010. - DOI
-
- Zhao Y.X., Kang D.J., Chen Z., Zhan J.J., Wu X.Q. Removal of Chromium Using Electrochemical Approaches: A Review. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2018;13:1250–1259. doi: 10.20964/2018.02.46. - DOI
Grants and funding
- 51805460/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2020H6003/Fujian Provincial Department of Science and Technology
- 2022H6036/Fujian Provincial Department of Science and Technology
- 2021J011196/Fujian Provincial Department of Science and Technology
- 2022A1515010923/Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

