Morpho-Structural Investigations and Carbon Nanoclustering Effects in Cr-Al-C Intermetallic Alloys
- PMID: 36145015
- PMCID: PMC9503499
- DOI: 10.3390/nano12183225
Morpho-Structural Investigations and Carbon Nanoclustering Effects in Cr-Al-C Intermetallic Alloys
Abstract
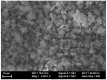
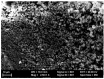
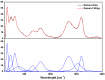
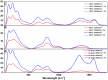
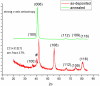
Intermetallic Cr-Al-C thin films from the 211 class of MAX phases were fabricated via ion beam deposition and structural investigations were undertaken to obtain information about morpho-structural effects propelled by carbon excess in the stoichiometry of the films. In order to promote the occurrence of the Cr2AlC MAX phase, the stoichiometric thin films were subsequently annealed at two temperature values: 650 °C and 700 °C in UHV conditions for 30 min. The morpho-structural effects in both as-deposited and annealed films were monitored using scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, and Raman spectroscopy. XRD analysis showed that the as-deposited sample was almost completely crystallized in the hexagonal Cr2AlC structure, with a remaining amorphous fraction of about 17%, most probably rich in carbon. Raman analysis allowed the identification of three spectral regions, two of them encompassing the Raman optical modes belonging to the Cr2AlC 211 MAX phase, while the third one gave strong evidence of highly intense and large D- and G-bands of carbon. Structural parameters such as the crystal lattice parameters as well as the volume of the crystal unit cell were found to decrease upon annealing; this decrease is attributed to the grain growth. The average crystallite dimension was proven to increase after annealing, while the lattice micro-strain lowered to approximately 63% in the annealed thin film compared to the as-deposited one. Well-formed and intense Raman peaks attributed to D- and G-bands of carbon were also observed and, corroborated with the structural data, seemed to indicate an overall increased level of crystal ordering as well as potential carbon nanoclustering after thermal treatments with thin Cr2AlC films. This observed phenomenon concords with previously documented reports on ab initio modelling of possible Cr2AlC structures with carbon excess.
Keywords: X-ray diffraction; annealing; carbon nanoclustering; crystallization; ternary alloys.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Jeitschko W., Nowotny H., Benesovsky F. Kohlenstoffhaltige ternäre Verbindungen (H-phase) Mon. Für Chem. Und Verwandte Teile And. Wiss. 1963;94:672–676. doi: 10.1007/BF00913068. - DOI
-
- Barsoum M.W., El-Raghy T. The MAX phases: Unique new carbide and nitride materials: Ternary ceramics turn out to be surprisingly soft and machinable, yet also heat-tolerant, strong and lightweight. Am. Sci. 2001;89:334–343. doi: 10.1511/2001.28.736. - DOI
-
- Eklund P., Beckers M., Jansson U., Högberg H., Hultman L. The Mn+1AXn phases: Materials science and thin-film processing. Thin Solid Film. 2010;518:1851–1878. doi: 10.1016/j.tsf.2009.07.184. - DOI
-
- Schneider J.M., Sun Z., Mertens R., Uestel F., Ahuja R. Ab initio calculations and experimental determination of the structure of Cr2AlC. Solid State Commun. 2004;130:445–449. doi: 10.1016/j.ssc.2004.02.047. - DOI
-
- Mertens R., Sun Z., Music D., Schneider J. Effect of the Composition on the Structure of Cr-Al-C Investigated by Combinatorial Thin Film Synthesis and ab Initio Calculations. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004;6:903–907. doi: 10.1002/adem.200400096. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

