Surface Layer Protein Pattern of Levilactobacillus brevis Strains Investigated by Proteomics
- PMID: 36145058
- PMCID: PMC9504196
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14183679
Surface Layer Protein Pattern of Levilactobacillus brevis Strains Investigated by Proteomics
Abstract
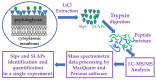
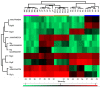
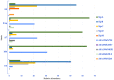
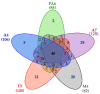
The outermost constituent of many bacterial cells is represented by an S-layer, i.e., a semiporous lattice-like layer composed of self-assembling protein subunits called S-layer proteins (Slps). These proteins are involved in several processes, such as protecting against environmental stresses, mediating bacterial adhesion to host cells, and modulating gut immune response. Slps may also act as a scaffold for the external display of additional cell surface proteins also named S-layer associated proteins (SLAPs). Levilactobacillus brevis is an S-layer forming lactic acid bacterium present in many different environments, such as sourdough, milk, cheese, and the intestinal tract of humans and animals. This microorganism exhibits probiotic features including the inhibition of bacterial infection and the improvement of human immune function. The potential role of Slps in its probiotic and biotechnological features was documented. A shotgun proteomic approach was applied to identify in a single experiment both the Slps and the SLAPs pattern of five different L. brevis strains isolated from traditional sourdoughs of the Southern Italian region. This study reveals that these closely related strains expressed a specific pattern of surface proteins, possibly affecting their peculiar properties.
Keywords: L. brevis; lactic acid bacteria; probiotics; proteomics; surface associated proteins; surface layer proteins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Hill C., Guarner F., Reid G., Gibson G.R., Merenstein D.J., Pot B., Morelli L., Canani R.B., Flint H.J., Salminen S., et al. Expert consensus document. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014;11:506–514. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2014.66. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

