From Diabetes Care to Heart Failure Management: A Potential Therapeutic Approach Combining SGLT2 Inhibitors and Plant Extracts
- PMID: 36145112
- PMCID: PMC9504067
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14183737
From Diabetes Care to Heart Failure Management: A Potential Therapeutic Approach Combining SGLT2 Inhibitors and Plant Extracts
Abstract
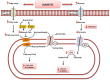
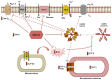
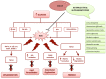
Diabetes is a complex chronic disease, and among the affected patients, cardiovascular disease (CVD)is the most common cause of death. Consequently, the evidence for the cardiovascular benefit of glycaemic control may reduce long-term CVD rates. Over the years, multiple pharmacological approaches aimed at controlling blood glucose levels were unable to significantly reduce diabetes-related cardiovascular events. In this view, a therapeutic strategy combining SGLT2 inhibitors and plant extracts might represent a promising solution. Indeed, countering the main cardiometabolic risk factor using plant extracts could potentiate the cardioprotective action of SGLT2 inhibitors. This review highlights the main molecular mechanisms underlying these beneficial effects that could contribute to the better management of diabetic patients.
Keywords: SGLT2 inhibitors; cardiovascular risk; diabetes; inflammation; insulin resistance; lipid accumulation; nutraceutical supplementation; reactive oxygen species (ROS).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Reid J.B. Re: Registry. Can we talk. Radiol. Technol. 1990;61:307–308. - PubMed
-
- Palmer S.C., Tendal B., Mustafa R.A., Vandvik P.O., Li S., Hao Q., Tunnicliffe D., Ruospo M., Natale P., Saglimbene V., et al. Sodium-glucose cotransporter protein-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists for type 2 diabetes: Systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ. 2021;372:m4573. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m4573. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

