Impact of COVID-19 Lockdown on Food Consumption and Behavior in France (COVISTRESS Study)
- PMID: 36145114
- PMCID: PMC9505280
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14183739
Impact of COVID-19 Lockdown on Food Consumption and Behavior in France (COVISTRESS Study)
Abstract
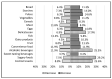
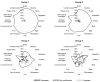
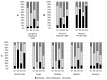
The COVID-19 pandemic and subsequent lockdowns modified work environments, lifestyles, and food consumption. Eating habits and mood changes in a French population during the first lockdown were examined using an online self-reported questionnaire with REDCap software through the COVISTRESS.ORG website. In 671 French participants, the main changes during lockdown were increased stress levels (64 [23; 86] vs. 3 [0; 18]) and sedentary behavior (7 [4; 9] vs. 5 [3; 8] hours per day), a deterioration in sleep quality (50 [27; 83] vs. 70 [48; 94]) and mood (50 [30; 76] vs. 78 [50; 92]), and less physical activity (2.0 [0.5; 5.0] vs. 3.5 [2.0; 6.0]). Mood was modified, with more anger (56 [39; 76] vs. 31 [16; 50]), more sadness (50 [34; 72] vs. 28 [16; 50]), more agitation (50 [25; 66] vs. 43 [20; 50]), and more boredom (32 [7; 60] vs. 14 [3; 29]). A total of 25% of the participants increased their consumption of alcoholic beverages, 29% their consumption of sugary foods, and 26% their consumption of cocktail snacks. A multiple-correspondence analysis highlights four different profiles according to changes in eating habits, food consumption, lifestyle, and mood. In conclusion, eating habits and lifestyle changes during lockdown periods should be carefully monitored to promote healthy behaviors.
Keywords: COVID-19; eating habits; lockdown.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Gorbalenya A.E., Baker S.C., Baric R.S., de Groot R.J., Drosten C., Gulyaeva A.A., Haagmans B.L., Lauber C., Leontovich A.M., Neuman B.W., et al. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-Related Coronavirus: The Species and Its Viruses—A Statement of the Coronavirus Study Group. bioRxiv. 2020 doi: 10.1101/2020.02.07.937862. - DOI
-
- Covid-19: Une Enquête Pour Suivre L’évolution des Comportements et de la Santé Mentale Pendant l’épidémie. [(accessed on 22 September 2020)]. Available online: https://www.santepubliquefrance.fr/etudes-et-enquetes/coviprev-une-enque....
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

