Enzobiotics-A Novel Therapy for the Elimination of Uremic Toxins in Patients with CKD (EETOX Study): A Multicenter Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 36145188
- PMCID: PMC9503043
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14183804
Enzobiotics-A Novel Therapy for the Elimination of Uremic Toxins in Patients with CKD (EETOX Study): A Multicenter Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
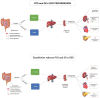
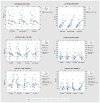
Design, participants, setting, and measurements: Predialysis adult participants with chronic kidney disease (CKD) and mean estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) <45 mL/min per 1.73 m2) were recruited in 2019 to a multicentric double-blinded randomized controlled trial of enzobiotic therapy (synbiotics and proteolytic enzymes) conducted over 12 weeks. The primary objective was to evaluate the efficacy and safety of enzobiotics in reducing the generation of p-cresol sulfate (PCS) and indoxyl sulfate (IS), stabilizing renal function, and improving quality of life (QoL), while the secondary objective was to evaluate the feasibility of the diagnostic prediction of IS and PCS from CKD parameters. Results: Of the 85 patients randomized (age 48.76 years, mean eGFR 23.24 mL/min per 1.73 m2 in the placebo group; age 54.03 years, eGFR 28.93 mL/min per 1.73 m2 in the enzobiotic group), 50 completed the study. The absolute mean value of PCS increased by 12% from 19 µg/mL (Day 0) to 21 µg/mL (Day90) for the placebo group, whereas it decreased by 31% from 23 µg/mL (Day 0) to 16 µg/mL (Day 90) for the enzobiotic group. For IS, the enzobiotic group showed a decrease (6.7%) from 11,668 to 10,888 ng/mL, whereas the placebo group showed an increase (8.8%) from 11,462 to 12,466 ng/mL (Day 90). Each patient improvement ratio for Day 90/Day 0 analysis showed that enzobiotics reduced PCS by 23% (0.77, p = 0.01). IS levels remained unchanged. In the placebo group, PCS increased by 27% (1.27, p = 0.14) and IS increased by 20% (1.20, p = 0.14). The proportion of individuals beyond the risk threshold for PCS (>20 µg/mL) was 53% for the placebo group and 32% for the enzobiotic group. The corresponding levels for IS risk (threshold >20,000 ng/mL) were 35% and 24% for the placebo and enzobiotic groups, respectively. In the placebo group, eGFR decreased by 7% (Day 90) but remained stable (1.00) in the enzobiotic group. QoL as assessed by the adversity ratio decreased significantly (p = 0.00), highlighting an improvement in the enzobiotic group compared to the placebo group. The predictive equations were as follows: PCS (Day 0 = −5.97 + 0.0453 PC + 2.987 UA − 1.310 Creat; IS (Day 0) = 756 + 1143 Creat + 436.0 Creat2. Conclusion: Enzobiotics significantly reduced the PCS and IS, as well as improved the QoL.
Keywords: SF-36-QoL; adversity ratio; eGFR; indoxyl sulfate; p-cresol; protein-bound uremic toxins (PBUTs).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Vanholder R., Meert N., Schepers E., Glorieux G., Argiles A., Brunet P., Cohen G., Drüeke T., Mischak H., Spasovski G., et al. Review on uraemic solutes II–variability in reported concentrations: Causes andconsequences. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2007;22:3115–3121. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfm151. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Miyazaki T., Ise M., Seo H., Niwa T. Indoxyl sulfate increases the gene expressions of tgf-beta 1, timp-1 and pro-alpha 1(i) collagen in uremic rat kidneys. Kidney Int. Suppl. 1997;62:S15–S22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

