The Challenge of Diagnosing and Managing Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in Systemic Sclerosis with Interstitial Lung Disease
- PMID: 36145263
- PMCID: PMC9504220
- DOI: 10.3390/ph15091042
The Challenge of Diagnosing and Managing Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in Systemic Sclerosis with Interstitial Lung Disease
Abstract
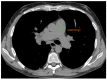
Pulmonary hypertension (PH) in patients with Systemic Sclerosis (SSc) may stem from a variety of underlying causes, thus making a correct diagnosis and management difficult. The main challenges lie in the distinction between pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH, group 1) and PH due to interstitial lung disease (PH-ILD, group 3) in patients with concomitant lung fibrosis — a very common occurrence in SSc. A consensus among experts remains elusive. Some studies have suggested that among SSc patients with PH, those with an ILD extension > 20% at high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) should be considered as affected by PH-ILD, whereas other Authors have found that a wide proportion of these patients exhibit features of both PAH and group 3 PH-ILD. We report the case of a 46-year-old male SSc patient with a stable and extensive ILD (>20%) who developed a histologically documented pulmonary vasculopathy typical of PAH and received PAH-specific treatment as bridge to transplant. Moreover, we documented PH disease course by right heart catheterization (RHC), with and without specific vasodilator therapies, which are essential in PAH but not indicated and/or harmful in PH-ILD.
Keywords: interstitial lung disease; pulmonary arterial hypertension; systemic sclerosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Clinical phenotypes, hemodynamic characteristics and prognosis of Chinese patients with systemic sclerosis-associated precapillary pulmonary hypertension: a retrospective study.Clin Rheumatol. 2022 Jun;41(6):1675-1686. doi: 10.1007/s10067-021-06016-8. Epub 2022 Jan 31. Clin Rheumatol. 2022. PMID: 35099674
-
Hemodynamic Response to Treatment and Outcomes in Pulmonary Hypertension Associated With Interstitial Lung Disease Versus Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in Systemic Sclerosis: Data From a Study Identifying Prognostic Factors in Pulmonary Hypertension Associated With Interstitial Lung Disease.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021 Feb;73(2):295-304. doi: 10.1002/art.41512. Epub 2020 Dec 29. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 32892515
-
Mortality and hospitalization outcomes of interstitial lung disease and pulmonary hypertension in the Singapore systemic sclerosis cohort.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2020 Jun;50(3):473-479. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2019.11.005. Epub 2019 Nov 13. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2020. PMID: 31810742
-
An Overview of Different Techniques for Improving the Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension Secondary in Systemic Sclerosis Patients.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Mar 1;12(3):616. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12030616. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35328169 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endothelial to mesenchymal transition (EndoMT) in the pathogenesis of Systemic Sclerosis-associated pulmonary fibrosis and pulmonary arterial hypertension. Myth or reality?Matrix Biol. 2016 Apr;51:26-36. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2016.01.012. Epub 2016 Jan 22. Matrix Biol. 2016. PMID: 26807760 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Special Issue "Rheumatic Diseases: Pathophysiology, Targeted Therapy, Focus on Vascular and Pulmonary Manifestations 2022".Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Apr 27;16(5):652. doi: 10.3390/ph16050652. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37242435 Free PMC article.
-
Serum Biomarkers in Connective Tissue Disease-Associated Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 20;24(4):4178. doi: 10.3390/ijms24044178. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835590 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in the Treatment of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Associated with Connective Tissue Diseases.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Sep 5;16(9):1252. doi: 10.3390/ph16091252. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37765060 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Galiè N., Humbert M., Vachiery J.L., Gibbs S., Lang I., Torbicki A., Simonneau G., Peacock A., Noordegraaf A.V., Beghetti M., et al. 2015 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: The Joint Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS): Endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC), International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT) Eur. Respir. J. 2015;46:903–975. - PubMed
-
- Young A., Vummidi D., Visovatti S., Homer K., Wilhalme H., White E.S., Flaherty K., McLaughlin V., Khanna D. Prevalence, Treatment, and Outcomes of Coexistent Pulmonary Hypertension and Interstitial Lung Disease in Systemic Sclerosis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019;71:1339–1349. doi: 10.1002/art.40862. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

