Binding of Natural Inhibitors to Respiratory Complex I
- PMID: 36145309
- PMCID: PMC9503403
- DOI: 10.3390/ph15091088
Binding of Natural Inhibitors to Respiratory Complex I
Abstract
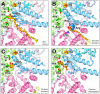
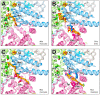
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (respiratory complex I) is a redox-driven proton pump with a central role in mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation. The ubiquinone reduction site of complex I is located in the matrix arm of this large protein complex and connected to the membrane via a tunnel. A variety of chemically diverse compounds are known to inhibit ubiquinone reduction by complex I. Rotenone, piericidin A, and annonaceous acetogenins are representatives of complex I inhibitors from biological sources. The structure of complex I is determined at high resolution, and inhibitor binding sites are described in detail. In this review, we summarize the state of knowledge of how natural inhibitors bind in the Q reduction site and the Q access pathway and how their inhibitory mechanisms compare with that of a synthetic anti-cancer agent.
Keywords: NADH dehydrogenase; Parkinson’s disease; acetogenin; mitochondria; piericidin; respiratory chain; rotenone.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

