In Silico Evaluation of CRISPR-Based Assays for Effective Detection of SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 36145402
- PMCID: PMC9506389
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens11090968
In Silico Evaluation of CRISPR-Based Assays for Effective Detection of SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
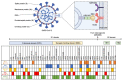
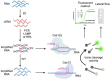
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) caused by the SARS-CoV-2 has been an outbreak since late 2019 up to now. This pandemic causes rapid development in molecular detection technologies to diagnose viral infection for epidemic prevention. In addition to antigen test kit (ATK) and polymerase chain reaction (PCR), CRISPR-based assays for detection of SARS-CoV-2 have gained attention because it has a simple setup but still maintain high specificity and sensitivity. However, the SARS-CoV-2 has been continuing mutating over the past few years. Thus, molecular tools that rely on matching at the nucleotide level need to be reevaluated to preserve their specificity and sensitivity. Here, we analyzed how mutations in different variants of concern (VOC), including Alpha, Beta, Gamma, Delta, and Omicron strains, could introduce mismatches to the previously reported primers and crRNAs used in the CRISPR-Cas system. Over 40% of the primer sets and 15% of the crRNAs contain mismatches. Hence, primers and crRNAs in nucleic acid-based assays must be chosen carefully to pair up with SARS-CoV-2 variants. In conclusion, the data obtained from this study could be useful in selecting the conserved primers and crRNAs for effective detections against the VOC of SARS-CoV-2.
Keywords: COVID-19; CRISPR; SARS-CoV-2; variants of concern.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Emergency SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern: Novel Multiplex Real-Time RT-PCR Assay for Rapid Detection and Surveillance.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Feb 23;10(1):e0251321. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02513-21. Epub 2022 Feb 23. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35196812 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR-Cas12a-Based Detection for the Major SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern.Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Dec 22;9(3):e0101721. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.01017-21. Epub 2021 Nov 17. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34787487 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR-Cas13d effectively targets SARS-CoV-2 variants, including Delta and Omicron, and inhibits viral infection.MedComm (2020). 2023 Jan 31;4(1):e208. doi: 10.1002/mco2.208. eCollection 2023 Feb. MedComm (2020). 2023. PMID: 36744219 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR techniques and potential for the detection and discrimination of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern.Trends Analyt Chem. 2023 Apr;161:117000. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2023.117000. Epub 2023 Mar 2. Trends Analyt Chem. 2023. PMID: 36937152 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Primer design for quantitative real-time PCR for the emerging Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2.Theranostics. 2020 Jun 1;10(16):7150-7162. doi: 10.7150/thno.47649. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32641984 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The role of cross-reactive immunity to emerging coronaviruses: Implications for novel universal mucosal vaccine design.Saudi Med J. 2023 Oct;44(10):965-972. doi: 10.15537/smj.2023.44.10.20230375. Saudi Med J. 2023. PMID: 37777266 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. [(accessed on 18 July 2022)]. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/
-
- World Health Organization Tracking SARS-CoV-2 Variants. [(accessed on 18 July 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/activities/tracking-SARS-CoV-2-variants.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

