MicroRNA-122 Regulation of HCV Infections: Insights from Studies of miR-122-Independent Replication
- PMID: 36145436
- PMCID: PMC9504723
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens11091005
MicroRNA-122 Regulation of HCV Infections: Insights from Studies of miR-122-Independent Replication
Abstract
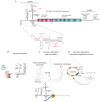
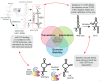
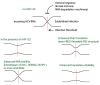
Despite the advancement in antiviral therapy, Hepatitis C remains a global health challenge and one of the leading causes of hepatitis related deaths worldwide. Hepatitis C virus, the causative agent, is a positive strand RNA virus that requires a liver specific microRNA called miR-122 for its replication. Unconventional to the canonical role of miRNAs in translation suppression by binding to 3'Untranslated Region (UTR) of messenger RNAs, miR-122 binds to two sites on the 5'UTR of viral genome and promotes viral propagation. In this review, we describe the unique relationship between the liver specific microRNA and HCV, the current knowledge on the mechanisms by which the virus uses miR-122 to promote the virus life cycle, and how miR-122 impacts viral tropism and pathogenesis. We will also discuss the use of anti-miR-122 therapy and its impact on viral evolution of miR-122-independent replication. This review further provides insight into how viruses manipulate host factors at the initial stage of infection to establish a successful infection.
Keywords: 5′ untranslated region; Hepatitis C virus; miR-122; miR-122-independent replication; viral tropism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

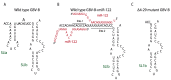
Similar articles
-
Enhanced Virus Translation Enables miR-122-Independent Hepatitis C Virus Propagation.J Virol. 2023 Jul 27;97(7):e0085821. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00858-21. Epub 2023 Jun 20. J Virol. 2023. PMID: 37338370 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of the Liver-Specific microRNA, miRNA-122 in the HCV Replication Cycle.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 7;21(16):5677. doi: 10.3390/ijms21165677. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32784807 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA 122 Affects both the Initiation and the Maintenance of Hepatitis C Virus Infections.J Virol. 2022 Feb 23;96(4):e0190321. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01903-21. Epub 2021 Dec 15. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 34908444 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Hepatitis C Virus Genome Replication by Xrn1 and MicroRNA-122 Binding to Individual Sites in the 5' Untranslated Region.J Virol. 2015 Jun;89(12):6294-311. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03631-14. Epub 2015 Apr 8. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25855736 Free PMC article.
-
[Hepatic tropism of hepatitis C virus infection].Uirusu. 2018;68(1):63-70. doi: 10.2222/jsv.68.63. Uirusu. 2018. PMID: 31105136 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA Nobel Prize: Timely Recognition and High Anticipation of Future Products-A Prospective Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 29;25(23):12883. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312883. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684593 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of MicroRNAs in Liver Functioning: from Biogenesis to Therapeutic Approaches (Review).Sovrem Tekhnologii Med. 2023;15(5):54-79. doi: 10.17691/stm2023.15.5.06. Epub 2023 Oct 30. Sovrem Tekhnologii Med. 2023. PMID: 39967915 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular regulators of alcoholic liver disease: a comprehensive analysis of microRNAs and long non-coding RNAs.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Mar 10;12:1482089. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1482089. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40130250 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Applications of Poly-miRNAs and miRNA Sponges.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 9;26(10):4535. doi: 10.3390/ijms26104535. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40429680 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A State-of-the-Art Review on the Recent Advances in Exosomes in Oncogenic Virus.Health Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 18;7(11):e70196. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.70196. eCollection 2024 Nov. Health Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39558933 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blach S., Zeuzem S., Manns M., Altraif I., Duberg A.-S., Muljono D.H., Waked I., Alavian S.M., Lee M.-H., Negro F., et al. Global prevalence and genotype distribution of hepatitis C virus infection in 2015: A modelling study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017;2:161–176. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Global Hepatitis Programme Global Hepatitis Report. [(accessed on 6 July 2022)];2017 Available online: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/255016/1/9789241565455-eng.pdf?....
-
- Chung R.T. Acute Hepatitis C Virus Infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005;41((Suppl. S1)):S14–S17. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

