Genetic Variants of Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase and Their Associated Enzyme Activity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 36145477
- PMCID: PMC9502867
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens11091045
Genetic Variants of Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase and Their Associated Enzyme Activity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
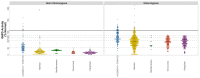
Low glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase enzyme (G6PD) activity is a key determinant of drug-induced haemolysis. More than 230 clinically relevant genetic variants have been described. We investigated the variation in G6PD activity within and between different genetic variants. In this systematic review, individual patient data from studies reporting G6PD activity measured by spectrophotometry and corresponding the G6PD genotype were pooled (PROSPERO: CRD42020207448). G6PD activity was converted into percent normal activity applying study-specific definitions of 100%. In total, 4320 individuals from 17 studies across 10 countries were included, where 1738 (40.2%) had one of the 24 confirmed G6PD mutations, and 61 observations (3.5%) were identified as outliers. The median activity of the hemi-/homozygotes with A-(c.202G>A/c.376A>G) was 29.0% (range: 1.7% to 76.6%), 10.2% (range: 0.0% to 32.5%) for Mahidol, 16.9% (range 3.3% to 21.3%) for Mediterranean, 9.0% (range: 2.9% to 23.2%) for Vanua Lava, and 7.5% (range: 0.0% to 18.3%) for Viangchan. The median activity in heterozygotes was 72.1% (range: 16.4% to 127.1%) for A-(c.202G>A/c.376A>G), 54.5% (range: 0.0% to 112.8%) for Mahidol, 37.9% (range: 20.7% to 80.5%) for Mediterranean, 53.8% (range: 10.9% to 82.5%) for Vanua Lava, and 52.3% (range: 4.8% to 78.6%) for Viangchan. A total of 99.5% of hemi/homozygotes with the Mahidol mutation and 100% of those with the Mediterranean, Vanua Lava, and Viangchan mutations had <30% activity. For A-(c.202G>A/c.376A>G), 55% of hemi/homozygotes had <30% activity. The G6PD activity for each variant spanned the current classification thresholds used to define clinically relevant categories of enzymatic deficiency.
Keywords: G6PD activity; G6PD deficiency; G6PD genotype; glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization . World Malaria Report 2020: 20 Years of Global Progress and Challenges. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2020.
-
- Battle K.E., Lucas T.C.D., Nguyen M., Howes R.E., Nandi A.K., Twohig K.A., Pfeffer D.A., Cameron E., Rao P.C., Casey D., et al. Mapping the global endemicity and clinical burden of Plasmodium vivax, 2000–2017: A spatial and temporal modelling study. Lancet. 2019 doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)31096-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

