Syphilis and Co-Infections with HIV-1, HBV, and HCV among People Who Use Crack-Cocaine in Northern Brazil
- PMID: 36145487
- PMCID: PMC9502650
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens11091055
Syphilis and Co-Infections with HIV-1, HBV, and HCV among People Who Use Crack-Cocaine in Northern Brazil
Abstract
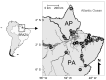
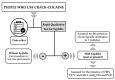
The rates of syphilis and viral co-infections among people who use crack-cocaine (PWUCC) were assessed in this study. This cross-sectional study relied on biological and self-reported socio-behavioral data from a convenience sample of 990 PWUCC from twenty-six municipalities in the states of Amapá and Pará, northern Brazil. Blood samples were collected to assess the presence of Treponema pallidum using the Rapid Qualitative Test (RQT) and the Venereal Disease Research Laboratory (VDRL). Reactive samples by RQT were used to assess the presence of HBV, HCV, and HIV-1 using Enzyme Immunoassay (EIA) and Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR). Logistic regression models were used to determine the association of variables assessed with syphilis. In total, 287 (29.0%) of the PWUCC sample had reactive results for syphilis. HBV (15.7%), HCV (5.9%), and HIV-1 (9.8%) were detected among PWUCC with syphilis. Young age, low monthly income and education level, long duration of crack-cocaine use, condomless sex, multiple sex partners, and exchange of sex for money/drugs were associated with syphilis. The present study provides unique insights on the epidemiological status of syphilis among PWUCC in northern Brazil, with multiple implications for improving urgent interventions for diagnosis, prevention, and treatment.
Keywords: Brazil; co-infections; crack-cocaine use; epidemiology; interventions; public health; syphilis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hepatitis E Virus in People Who Use Crack-Cocaine: A Cross-Sectional Study in a Remote Region of Northern Brazil.Viruses. 2021 May 17;13(5):926. doi: 10.3390/v13050926. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34067873 Free PMC article.
-
Oral HPV among people who use crack-cocaine: prevalence, genotypes, risk factors, and key interventions in a remote Northern Brazilian region.Clin Oral Investig. 2021 Feb;25(2):759-767. doi: 10.1007/s00784-020-03698-3. Epub 2020 Nov 22. Clin Oral Investig. 2021. PMID: 33222054
-
Screening for HBV, HCV, HIV and syphilis infections among bacteriologically confirmed tuberculosis prisoners: An urgent action required.PLoS One. 2019 Aug 22;14(8):e0221265. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0221265. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31437184 Free PMC article.
-
Serosurvey of anti-treponema pallidum (syphilis), anti-hepatitis C virus and anti-HIV antibodies in homeless persons of São Paulo city, southeastern Brazil.Braz J Infect Dis. 2021 Jul-Aug;25(4):101602. doi: 10.1016/j.bjid.2021.101602. Epub 2021 Aug 10. Braz J Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 34389284 Free PMC article.
-
Sero-epidemiology and associated factors of HIV, HBV, HCV and syphilis among blood donors in Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Infect Dis. 2021 Aug 9;21(1):778. doi: 10.1186/s12879-021-06505-w. BMC Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 34372772 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Seroprevalence and associated factors of HIV, syphilis, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C infections among sex workers in Chiangmai, Thailand during easing of COVID-19 lockdown measures.PLoS One. 2024 Dec 31;19(12):e0316668. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0316668. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39739911 Free PMC article.
References
-
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime World Drug Report 2021. 4 Drug Market Trends: Cocaine, Amphetamine-Type Stimulants. [(accessed on 13 July 2022)]. Available online: https://www.unodc.org/res/wdr2021/field/WDR21_Booklet_4.pdf.
-
- Bastos F.I., Vasconcelos M.T.L., De Boni R.B., Coutinho C.F.S. III Levantamento Nacional Sobre O Uso de Drogas Pela População Brasileira. [(accessed on 13 July 2022)]. Available online: https://www.arca.fiocruz.br/handle/icict/34614.
-
- Bastos F.I., Bertoni N. Pesquisa Nacional Sobre O Uso de Crack: Quem São Os Usuários de Crack E/Ou Similares Do Brasil? Quantos São Nas Capitais Brasileiras? [(accessed on 13 July 2022)]. Available online: https://www.arca.fiocruz.br/handle/icict/10019.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

