Inhibitory Effect of Periodontitis through C/EBP and 11β-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase Type 1 Regulation of Betulin Isolated from the Bark of Betula platyphylla
- PMID: 36145616
- PMCID: PMC9502078
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14091868
Inhibitory Effect of Periodontitis through C/EBP and 11β-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase Type 1 Regulation of Betulin Isolated from the Bark of Betula platyphylla
Abstract
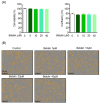
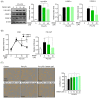
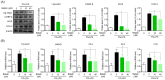
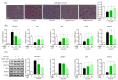
Periodontitis is an infectious inflammatory disease of the tissues around the tooth that destroys connective tissue and is characterized by loss of periodontal ligaments and alveolar bone. Currently, surgical methods for the treatment of periodontitis have limitations and new treatment strategies are needed. Therefore, this study evaluated the efficacy of the compound betulin isolated from bark of Betula platyphylla on the inhibition of periodontitis in vitro and in vivo periodontitis induction models. In the study, betulin inhibited pro-inflammatory mediators, such as tumor necrosis factor, interleukin-6, inducible nitric oxide synthase, and cyclooxygenase-2, in human periodontal ligament cells stimulated with Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide (PG-LPS). In addition, it showed an anti-inflammatory effect by down-regulating 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 and transcription factor C/EBP β produced by PG-LPS. Moreover, PG-LPS inhibited the osteogenic induction of human periodontal ligament cells. The protein and mRNA levels of osteogenic markers, such as inhibited osteopontin (OPN) and runt-related transcription factor 2 (RUNX2), were regulated by betulin. In addition, the efficacy of betulin was demonstrated in a typical in vivo model of periodontitis induced by PG-LPS, and the results showed through hematoxylin & eosin staining and micro-computed tomography that the administration of betulin alleviated alveolar bone loss and periodontal inflammation caused by PG-LPS. Therefore, this study proved the efficacy of the compound betulin isolated from B. platyphylla in the inhibition of periodontitis and alveolar bone loss, two important strategies for the treatment of periodontitis, suggesting the potential as a new treatment for periodontitis.
Keywords: 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1; betulin; human periodontal ligament cells; inflammation; osteogenic induction; periodontitis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Panax ginseng Fruit Has Anti-Inflammatory Effect and Induces Osteogenic Differentiation by Regulating Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway in In Vitro and In Vivo Models of Periodontitis.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Dec 3;9(12):1221. doi: 10.3390/antiox9121221. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33287198 Free PMC article.
-
New Application of Psoralen and Angelicin on Periodontitis With Anti-bacterial, Anti-inflammatory, and Osteogenesis Effects.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018 Jun 5;8:178. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2018.00178. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29922598 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Effects of Hinokitiol through Regulating the SIRT1/NOX4 against Ligature-Induced Experimental Periodontitis.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Apr 30;13(5):550. doi: 10.3390/antiox13050550. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38790655 Free PMC article.
-
[microRNA-146a reverses the inhibitory effects of Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide on osteogenesis of human periodontal ligament cells].Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2018 Nov 9;53(11):753-759. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1002-0098.2018.11.007. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 30419656 Chinese.
-
[Relationhip between diabetes and periodontal disease].Clin Calcium. 2009 Sep;19(9):1291-8. Clin Calcium. 2009. PMID: 19721200 Review. Japanese.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

