The Impact of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme-2/Angiotensin 1-7 Axis in Establishing Severe COVID-19 Consequences
- PMID: 36145655
- PMCID: PMC9505151
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14091906
The Impact of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme-2/Angiotensin 1-7 Axis in Establishing Severe COVID-19 Consequences
Abstract
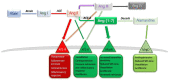
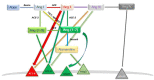
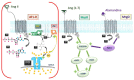
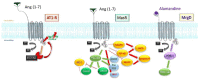
The COVID-19 pandemic has put a tremendous stress on the medical community over the last two years. Managing the infection proved a lot more difficult after several research communities started to recognize the long-term effects of this disease. The cellular receptor for the virus was identified as angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (ACE2), a molecule responsible for a wide array of processes, broadly variable amongst different organs. Angiotensin (Ang) 1-7 is the product of Ang II, a decaying reaction catalysed by ACE2. The effects observed after altering the level of ACE2 are essentially related to the variation of Ang 1-7. The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) is comprised of two main branches, with ACE2 representing a crucial component of the protective part of the complex. The ACE2/Ang (1-7) axis is well represented in the testis, heart, brain, kidney, and intestine. Infection with the novel SARS-CoV-2 virus determines downregulation of ACE2 and interrupts the equilibrium between ACE and ACE2 in these organs. In this review, we highlight the link between the local effects of RAAS and the consequences of COVID-19 infection as they arise from observational studies.
Keywords: ACE2; Ang (1-7); COVID-19; RAAS; angiotensin 1-7; angiotensin-converting enzyme-2; long-term effects; renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The RAAS Axis and SARS-CoV-2: From Oral to Systemic Manifestations.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Nov 24;58(12):1717. doi: 10.3390/medicina58121717. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 36556919 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunohistochemical and Transcriptional Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Entry Factors and Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Components in Lethal COVID-19.Pathobiology. 2022;89(3):166-177. doi: 10.1159/000520221. Epub 2021 Dec 16. Pathobiology. 2022. PMID: 34915500 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulation of ACE (Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme)-2 and Renin-Angiotensin Peptides in SARS-CoV-2 Mediated Mortality and End-Organ Injuries.Hypertension. 2022 Feb;79(2):365-378. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.121.18295. Epub 2021 Nov 30. Hypertension. 2022. PMID: 34844421
-
Recent Update of Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone System in the Pathogenesis of Hypertension.Electrolyte Blood Press. 2013 Dec;11(2):41-5. doi: 10.5049/EBP.2013.11.2.41. Epub 2013 Dec 31. Electrolyte Blood Press. 2013. PMID: 24627703 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Renin Angiotensin Axis, Angiotensin Converting Enzyme 2 and Coronavirus].Rev Chil Pediatr. 2020 Jun;91(3):330-338. doi: 10.32641/rchped.vi91i3.2548. Rev Chil Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 32730512 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
Epicardial Adipose Tissue as a Prognostic Marker in COVID-19.In Vivo. 2024 Jan-Feb;38(1):281-285. doi: 10.21873/invivo.13436. In Vivo. 2024. PMID: 38148083 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the Role of the Renin-angiotensin System in COVID-19: Implications for ACE Inhibitor and ARB Use During SARS-CoV-2 Infection.J Cell Immunol. 2024;6(6):255-265. doi: 10.33696/immunology.6.213. J Cell Immunol. 2024. PMID: 40417281 Free PMC article.
-
Farnesoid X receptor enhances epithelial ACE2 expression and inhibits virally induced IL-6 secretion: implications for intestinal symptoms of SARS-CoV-2.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2023 Nov 1;325(5):G446-G452. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00099.2023. Epub 2023 Sep 12. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37697930 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of oral 20-hydroxyecdysone (BIO101), a MAS receptor activator, in adults with severe COVID-19 (COVA): a randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 2/3 trial.EClinicalMedicine. 2024 Jan 3;68:102383. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.102383. eCollection 2024 Feb. EClinicalMedicine. 2024. PMID: 38545090 Free PMC article.
-
Endotheliopathy in Acute COVID-19 and Long COVID.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 4;24(9):8237. doi: 10.3390/ijms24098237. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37175942 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

