Antimicrobial Peptides and Biomarkers Induced by Ultraviolet Irradiation Have the Potential to Reduce Endodontic Inflammation and Facilitate Tissue Healing
- PMID: 36145725
- PMCID: PMC9503046
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14091979
Antimicrobial Peptides and Biomarkers Induced by Ultraviolet Irradiation Have the Potential to Reduce Endodontic Inflammation and Facilitate Tissue Healing
Abstract
Background: Ultraviolet (UV) irradiation can modulate host immune responses and this approach is a novel application for treating endodontic infections and inflammation in root canals.
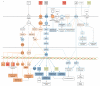
Methods: A dataset of UV-induced molecules was compiled from a literature search. A subset of this dataset was used to calculate expression log2 ratios of endodontic tissue molecules from HEPM cells and gingival fibroblasts after 255, 405, and 255/405 nm UV irradiation. Both datasets were analyzed using ingenuity pathway analysis (IPA, Qiagen, Germantown, MD, USA). Statistical significance was calculated using Fisher's exact test and z-scores were calculated for IPA comparison analysis.
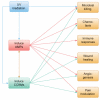
Results: The dataset of 32 UV-induced molecules contained 9 antimicrobial peptides, 10 cytokines, 6 growth factors, 3 enzymes, 2 transmembrane receptors, and 2 transcription regulators. These molecules were in the IPA canonical pathway annotations for the wound healing signaling pathway (9/32, p = 3.22 × 10-11) and communication between immune cells (6/32, p = 8.74 × 10-11). In the IPA disease and function annotations, the 32 molecules were associated with an antimicrobial response, cell-to-cell signaling and interaction, cellular movement, hematological system development and function, immune cell trafficking, and inflammatory response. In IPA comparison analysis of the 13 molecules, the predicted activation or inhibition of pathways depended upon the cell type exposed, the wavelength of the UV irradiation used, and the time after exposure.
Conclusions: UV irradiation activates and inhibits cellular pathways and immune functions. These results suggested that UV irradiation can activate innate and adaptive immune responses, which may supplement endodontic procedures to reduce infection, inflammation, and pain and assist tissues to heal.
Keywords: UV; UVA; UVB; UVC; antimicrobial peptides; chemokines; cytokines; endodontic; inflammation; pain; tissue healing; ultraviolet irradiation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. We have no financial affiliation (e.g., employment, direct payment, stock holdings, retainers, consultantships, patent licensing arrangements, or honoraria), or involvement with any commercial organization with direct financial interest in the subject or materials discussed in this manuscript, nor have any such arrangements existed in the past 3 years. Kimberly A. Morio is an Endodontist at Apex Endodontics and an Adjunct Instructor at the University of Iowa; Robert H. Sternowski is the President of Softronics, Ltd.; Erliang Zeng is a Biostatistician and a Computational Biologist at the University of Iowa; and Kim A. Brogden is an Emeritus Professor at the University of Iowa. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results. The company had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Induction of Endogenous Antimicrobial Peptides to Prevent or Treat Oral Infection and Inflammation.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Feb 9;12(2):361. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12020361. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36830272 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dataset of endodontic microorganisms killed at 265 nm wavelength by an ultraviolet C light emitting diode in root canals of extracted, instrumented teeth.Data Brief. 2021 Dec 23;40:107750. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2021.107750. eCollection 2022 Feb. Data Brief. 2021. PMID: 35024392 Free PMC article.
-
UVB and UVC, but not UVA, potently induce the appearance of T6- DR+ antigen-presenting cells in human epidermis.J Invest Dermatol. 1987 Jul;89(1):113-8. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12580461. J Invest Dermatol. 1987. PMID: 3598201
-
Genome-wide analysis of DNA methylation in UVB- and DMBA/TPA-induced mouse skin cancer models.Life Sci. 2014 Sep 15;113(1-2):45-54. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2014.07.031. Epub 2014 Aug 2. Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 25093921 Free PMC article.
-
Ultraviolet Radiation in Wound Care: Sterilization and Stimulation.Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2013 Oct;2(8):422-437. doi: 10.1089/wound.2012.0366. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2013. PMID: 24527357 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Induction of Endogenous Antimicrobial Peptides to Prevent or Treat Oral Infection and Inflammation.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Feb 9;12(2):361. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12020361. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36830272 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Editorial Position on 'Recent Advances in Multifunctional Antimicrobial Peptides as Preclinical Therapeutic Studies and Clinical Future Applications'.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Sep 26;15(10):2383. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15102383. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37896143 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Delikan E., Caliskan S., Cankilic M.Y., Aksu S., Kesim B., Ulger S.T. Microbiota of endodontically infected primary and permanent teeth. Pediatr. Dent. 2021;43:102–110. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

