Combined Pulsed Electric Field and Microwave-Assisted Extraction as a Green Method for the Recovery of Antioxidant Compounds with Electroactive Potential from Coffee Agro-Waste
- PMID: 36145763
- PMCID: PMC9505628
- DOI: 10.3390/plants11182362
Combined Pulsed Electric Field and Microwave-Assisted Extraction as a Green Method for the Recovery of Antioxidant Compounds with Electroactive Potential from Coffee Agro-Waste
Abstract
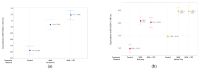
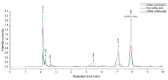
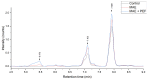
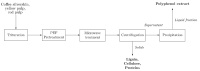
Coffee agro-waste is a potential source of polyphenols with antioxidant activity and application in the food and cosmetic trades. The usage of these byproducts persists as a challenge in the industrial landscape due to their high content of purported toxic substances hindering management. This study presents a green extractive process using pulsed electric field (PEF) and microwave assisted extraction (MAE) to recover polyphenols from coffee parchment and two varieties of pulp, posing quick processing times and the use of water as the only solvent. The performance of this process with regard to the bioactivity was assessed through the Folin-Ciocalteu assay, total flavonoid content, DPPH, ABTS and FRAP antioxidant tests. The phenolic composition of the extracts was also determined through HPLC-MS and quantified through HPLC-DAD. When compared to treatment controls, PEF + MAE treated samples presented enhanced yields of total phenolic content and radical scavenging activity in all analyzed residues (Tukey test significance: 95%). The chromatographic studies reveal the presence of caffeic acid on the three analyzed by-products. The HPLC-DAD caffeic acid quantification validated that a combination of MAE + PEF treatment in yellow coffee pulp had the highest caffeic acid concentration of all studied extraction methods.
Keywords: coffee agrowaste; microwave-assisted extraction; polyphenols; pulsed electric fields; solvent-free extraction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Cerino-Córdova F.J., Dávila-Guzmán N.E., León A.M.G., Salazar-Rabago J.J., Soto-Regalado E. Revalorization of Coffee Waste. IntechOpen; London, UK: 2020.
-
- International Coffee Organization June 2022 Coffee Market Report. [(accessed on 9 September 2022)]. Available online: https://www.ico.org/Market-Report-21-22-e.asp.
-
- González Razo F.D.J., Sangerman-Jarquín D.M., Rebollar Rebollar S., Omaña Silvestre J.M., Hernández Martínez J., Morales Hernández J.L., González Razo F.D.J., Sangerman-Jarquín D.M., Rebollar Rebollar S., Omaña Silvestre J.M., et al. The Coffee Marketing Process in the South of the State of Mexico. Rev. Mex. Cienc. Agríc. 2019;10:1195–1206. doi: 10.29312/remexca.v10i6.2057. - DOI
-
- Arana-Coronado J.J., Trejo-Pech C.O., Velandia M., Peralta-Jimenez J. Factors Influencing Organic and Fair Trade Coffee Growers Level of Engagement with Cooperatives: The Case of Coffee Farmers in Mexico. J. Int. Food Agribus. Mark. 2019;31:22–51. doi: 10.1080/08974438.2018.1471637. - DOI
-
- Secretaría de Agricultura y Desarrollo Rural México, Onceavo Productor Mundial de Café. [(accessed on 11 July 2021)]. Available online: http://www.gob.mx/agricultura/es/articulos/mexico-onceavo-productor-mund....
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

