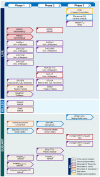
The Shigella Vaccines Pipeline
- PMID: 36146457
- PMCID: PMC9504713
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines10091376
The Shigella Vaccines Pipeline
Abstract
Shigella is the leading cause of global diarrheal deaths that currently lacks a licensed vaccine. Shigellosis drives antimicrobial resistance and leads to economic impact through linear growth faltering. Today, there is a robust pipeline of vaccines in clinical development which are broadly divided into parenteral glycoconjugate vaccines, consisting of O-antigen conjugated to carrier proteins, and oral live attenuated vaccines, which incorporate targeted genetic mutations seeking to optimize the balance between reactogenicity, immunogenicity and ultimately protection. Proof of efficacy has previously been shown with both approaches but for various reasons no vaccine has been licensed to date. In this report, we outline the requirements for a Shigella vaccine and describe the current pipeline in the context of the many candidates that have previously failed or been abandoned. The report refers to papers from individual vaccine developers in this special supplement of Vaccines which is focused on Shigella vaccines. Once readouts of safety and immunogenicity from current trials of lead candidate vaccines among the target population of young children in low- and middle-income countries are available, the likely time to licensure of a first Shigella vaccine will become clearer.
Keywords: Shigella; diarrhea; dysentery; flexneri; global health; glycoconjugate; live attenuated; shigellosis; sonnei; vaccines.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kotloff K.L., Nataro J.P., Blackwelder W.C., Nasrin D., Farag T.H., Panchalingam S., Wu Y., Sow S.O., Sur D., Breiman R.F., et al. Burden and aetiology of diarrhoeal disease in infants and young children in developing countries (the Global Enteric Multicenter Study, GEMS): A prospective, case-control study. Lancet. 2013;382:209–222. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60844-2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Liu J., Platts-Mills J.A., Juma J., Kabir F., Nkeze J., Okoi C., Operario D.J., Uddin J., Ahmed S., Alonso P.L., et al. Use of quantitative molecular diagnostic methods to identify causes of diarrhoea in children: A reanalysis of the GEMS case-control study. Lancet. 2016;388:1291–1301. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31529-X. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Platts-Mills J.A., Liu J., Rogawski E.T., Kabir F., Lertsethtakarn P., Siguas M., Khan S.S., Praharaj I., Murei A., Nshama R., et al. Use of quantitative molecular diagnostic methods to assess the aetiology, burden, and clinical characteristics of diarrhoea in children in low-resource settings: A reanalysis of the MAL-ED cohort study. Lancet Glob. Health. 2018;6:e1309–e1318. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(18)30349-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical