Microneedle Delivery of an Adjuvanted Microparticulate Vaccine Induces High Antibody Levels in Mice Vaccinated against Coronavirus
- PMID: 36146568
- PMCID: PMC9503342
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines10091491
Microneedle Delivery of an Adjuvanted Microparticulate Vaccine Induces High Antibody Levels in Mice Vaccinated against Coronavirus
Abstract
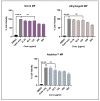
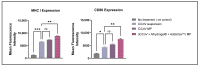
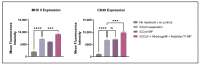
This 'proof-of-concept' study aimed to test the microparticulate vaccine delivery system and a transdermal vaccine administration strategy using dissolving microneedles (MN). For this purpose, we formulated poly(lactic-co-glycolic) acid (PLGA) microparticles (MP) encapsulating the inactivated canine coronavirus (iCCoV), as a model antigen, along with adjuvant MP encapsulating Alhydrogel® and AddaVax. We characterized the vaccine MP for size, surface charge, morphology, and encapsulation efficiency. Further, we evaluated the in vitro immunogenicity, cytotoxicity, and antigen-presentation of vaccine/adjuvant MP in murine dendritic cells (DCs). Additionally, we tested the in vivo immunogenicity of the MP vaccine in mice through MN administration. We evaluated the serum IgG, IgA, IgG1, and IgG2a responses using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The results indicate that the particulate form of the vaccine is more immunogenic than the antigen suspension in vitro. We found the vaccine/adjuvant MP to be non-cytotoxic to DCs. The expression of antigen-presenting molecules, MHC I/II, and their costimulatory molecules, CD80/40, increased with the addition of the adjuvants. Moreover, the results suggest that the MP vaccine is cross presented by the DCs. In vivo, the adjuvanted MP vaccine induced increased antibody levels in mice following vaccination and will further be assessed for its cell-mediated responses.
Keywords: antibody response; antigen presentation; cytotoxicity; immunogenicity; microneedles; microparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest. The authors are responsible for the contents and writing of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An Adjuvanted Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Microparticulate Vaccine Delivered Using Microneedles Induces a Robust Immune Response in Vaccinated Mice.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Mar 9;15(3):895. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15030895. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36986756 Free PMC article.
-
Novel microparticulate Zika vaccine induces a significant immune response in a preclinical murine model after intramuscular administration.Int J Pharm. 2022 Aug 25;624:121975. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2022.121975. Epub 2022 Jul 3. Int J Pharm. 2022. PMID: 35787459
-
Subunit microparticulate vaccine delivery using microneedles trigger significant SARS-spike-specific humoral and cellular responses in a preclinical murine model.Int J Pharm. 2023 Feb 5;632:122583. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2023.122583. Epub 2023 Jan 4. Int J Pharm. 2023. PMID: 36610521 Free PMC article.
-
Microneedle Delivery of Heterologous Microparticulate COVID-19 Vaccine Induces Cross Strain Specific Antibody Levels in Mice.Vaccines (Basel). 2025 Apr 1;13(4):380. doi: 10.3390/vaccines13040380. Vaccines (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40333230 Free PMC article.
-
PLGA particulate delivery systems for subunit vaccines: Linking particle properties to immunogenicity.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2016 Apr 2;12(4):1056-69. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2015.1117714. Epub 2016 Jan 11. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2016. PMID: 26752261 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluating Nanoparticulate Vaccine Formulations for Effective Antigen Presentation and T-Cell Proliferation Using an In Vitro Overlay Assay.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Sep 13;12(9):1049. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12091049. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39340079 Free PMC article.
-
Adjuvanted-SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein-Based Microparticulate Vaccine Delivered by Dissolving Microneedles Induces Humoral, Mucosal, and Cellular Immune Responses in Mice.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Aug 10;16(8):1131. doi: 10.3390/ph16081131. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37631046 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccine-Induced Immunity Elicited by Microneedle Delivery of Influenza Ectodomain Matrix Protein 2 Virus-like Particle (M2e VLP)-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 25;24(13):10612. doi: 10.3390/ijms241310612. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37445784 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the Immunogenicity of an Intranasal Microparticle Combination Vaccine for COVID-19 and Influenza.Vaccines (Basel). 2025 Mar 7;13(3):282. doi: 10.3390/vaccines13030282. Vaccines (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40266139 Free PMC article.
-
An Adjuvanted Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Microparticulate Vaccine Delivered Using Microneedles Induces a Robust Immune Response in Vaccinated Mice.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Mar 9;15(3):895. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15030895. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36986756 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

