T-Cell Responses Induced by an Intradermal BNT162b2 mRNA Vaccine Booster Following Primary Vaccination with Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine
- PMID: 36146571
- PMCID: PMC9501140
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines10091494
T-Cell Responses Induced by an Intradermal BNT162b2 mRNA Vaccine Booster Following Primary Vaccination with Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine
Abstract
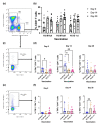
A practical booster vaccine is urgently needed to control the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic. We have previously reported the safety and immunogenicity of a fractional intradermal booster, using the BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine in healthy volunteers who had completed two doses of inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. In this study, an intramuscular booster at full dosage was used as a control, and a half-dose vaccination was included for reciprocal comparison. Detailed T-cell studies are essential to understand cellular responses to vaccination. T-cell immunity was examined using S1 peptide restimulation and flow cytometry. The fractional dose (1:5) of the BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine enhanced antigen-specific effector T-cells, but the responses were less remarkable compared to the intramuscular booster at full dosage. However, the intradermal regimen was not inferior to the intramuscular booster a month after boosting. An intradermal booster using only one-fifth of the standard dosage could provide comparable T-cell responses with the fractional intramuscular booster. This work confirms the efficacy of intradermal and fractional vaccination in terms of T-cell immunogenicity in previously immunised populations.
Keywords: COVID-19; T-cells; inactivated SARS-CoV-2; intradermal; mRNA vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial or non-financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Pandemic. [(accessed on 21 June 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/europe/emergencies/situations/covid-19.
-
- World Health Organization Timeline: WHO’s COVID-19 Response. [(accessed on 21 June 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/interact....
-
- World Health Organization WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. [(accessed on 1 July 2022)]. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/?mapFilter=cases.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

