An Efficacious Transgenic Strategy for Triple Knockout of Xeno-Reactive Antigen Genes GGTA1, CMAH, and B4GALNT2 from Jeju Native Pigs
- PMID: 36146581
- PMCID: PMC9505423
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines10091503
An Efficacious Transgenic Strategy for Triple Knockout of Xeno-Reactive Antigen Genes GGTA1, CMAH, and B4GALNT2 from Jeju Native Pigs
Abstract
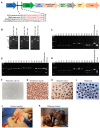
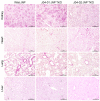
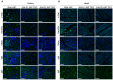
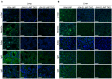
Pigs are promising donors of biological materials for xenotransplantation; however, cell surface carbohydrate antigens, including galactose-alpha-1,3-galactose (α-Gal), N-glycolylneuraminic acid (Neu5Gc), and Sd blood group antigens, play a significant role in porcine xenograft rejection. Inactivating swine endogenous genes, including GGTA1, CMAH, and B4GALNT2, decreases the binding ratio of human IgG/IgM in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and erythrocytes and impedes the effectiveness of α-Gal, Neu5Gc, and Sd, thereby successfully preventing hyperacute rejection. Therefore, in this study, an effective transgenic system was developed to target GGTA1, CMAH, and B4GALNT2 using CRISPR-CAS9 and develop triple-knockout pigs. The findings revealed that all three antigens (α-Gal, Neu5Gc, and Sd) were not expressed in the heart, lungs, or liver of the triple-knockout Jeju Native Pigs (JNPs), and poor expression of α-Gal and Neu5G was confirmed in the kidneys. Compared with the kidney, heart, and lung tissues from wild-type JNPs, those from GGTA1/CMAH/ B4GALNT2 knockout-recipient JNPs exhibited reduced human IgM and IgG binding and expression of each immunological rejection component. Hence, reducing the expression of swine xenogeneic antigens identifiable by human immunoglobulins can lessen the immunological rejection against xenotransplantation. The findings support the possibility of employing knockout JNP organs for xenogeneic transplantation to minimize or completely eradicate rejection using multiple gene-editing methods.
Keywords: CRISPR-CAS9 system; Jeju native pigs; immune rejection; xenotransplantation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Viable pigs after simultaneous inactivation of porcine MHC class I and three xenoreactive antigen genes GGTA1, CMAH and B4GALNT2.Xenotransplantation. 2020 Jan;27(1):e12560. doi: 10.1111/xen.12560. Epub 2019 Oct 8. Xenotransplantation. 2020. PMID: 31591751
-
Erythrocytes from GGTA1/CMAH knockout pigs: implications for xenotransfusion and testing in non-human primates.Xenotransplantation. 2014 Jul-Aug;21(4):376-84. doi: 10.1111/xen.12106. Epub 2014 Jul 2. Xenotransplantation. 2014. PMID: 24986655 Free PMC article.
-
Reducing immunoreactivity of porcine bioprosthetic heart valves by genetically-deleting three major glycan antigens, GGTA1/β4GalNT2/CMAH.Acta Biomater. 2018 May;72:196-205. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2018.03.055. Epub 2018 Apr 7. Acta Biomater. 2018. PMID: 29631050
-
B4GALNT2 and xenotransplantation: A newly appreciated xenogeneic antigen.Xenotransplantation. 2018 Sep;25(5):e12394. doi: 10.1111/xen.12394. Epub 2018 Mar 31. Xenotransplantation. 2018. PMID: 29604134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress in multiple genetically modified minipigs for xenotransplantation in China.Xenotransplantation. 2019 Jan;26(1):e12492. doi: 10.1111/xen.12492. Xenotransplantation. 2019. PMID: 30775816 Review.
Cited by
-
Developments in kidney xenotransplantation.Front Immunol. 2024 Jan 11;14:1242478. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1242478. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38274798 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elimination of GGTA1, CMAH, β4GalNT2 and CIITA genes in pigs compromises human versus pig xenogeneic immune reactions.Animal Model Exp Med. 2024 Aug;7(4):584-590. doi: 10.1002/ame2.12461. Epub 2024 Jul 4. Animal Model Exp Med. 2024. PMID: 38962826 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental Swine Models for Vascularized Composite Allotransplantation and Immunosuppression: A Systematic Review and Case Report of a Novel Heterotopic Hemifacial Swine Model.Transpl Int. 2025 Jul 29;38:14520. doi: 10.3389/ti.2025.14520. eCollection 2025. Transpl Int. 2025. PMID: 40799314 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging and potential use of CRISPR in human liver disease.Hepatology. 2025 Jul 1;82(1):232-253. doi: 10.1097/HEP.0000000000000578. Epub 2025 Jun 19. Hepatology. 2025. PMID: 37607734 Review.
-
Influence of relatively short-term culture on adult porcine islets for xenotransplantation.Sci Rep. 2024 May 21;14(1):11640. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-62570-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38773268 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Oura T., Hotta K., Lei J., Markmann J., Rosales I., Dehnadi A., Kawai K., Ndishabandi D., Smith R.-N., Cosimi A.B., et al. Immunosuppression With CD40 Costimulatory Blockade Plus Rapamycin for Simultaneous Islet-Kidney Transplantation in Nonhuman Primates. Am. J. Transplant. 2017;17:646–656. doi: 10.1111/ajt.13999. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

