Role of RNA Polymerase II Promoter-Proximal Pausing in Viral Transcription
- PMID: 36146833
- PMCID: PMC9503719
- DOI: 10.3390/v14092029
Role of RNA Polymerase II Promoter-Proximal Pausing in Viral Transcription
Abstract
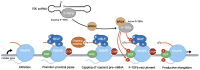
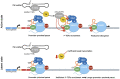
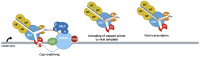
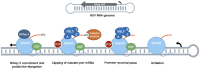
The promoter-proximal pause induced by the binding of the DRB sensitivity-inducing factor (DSIF) and the negative elongation factor (NELF) to RNAP II is a key step in the regulation of metazoan gene expression. It helps maintain a permissive chromatin landscape and ensures a quick transcriptional response from stimulus-responsive pathways such as the innate immune response. It is also involved in the biology of several RNA viruses such as the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), the influenza A virus (IAV) and the hepatitis delta virus (HDV). HIV uses the pause as one of its mechanisms to enter and maintain latency, leading to the creation of viral reservoirs resistant to antiretrovirals. IAV, on the other hand, uses the pause to acquire the capped primers necessary to initiate viral transcription through cap-snatching. Finally, the HDV RNA genome is transcribed directly by RNAP II and requires the small hepatitis delta antigen to displace NELF from the polymerase and overcome the transcriptional block caused by RNAP II promoter-proximal pausing. In this review, we will discuss the RNAP II promoter-proximal pause and the roles it plays in the life cycle of RNA viruses such as HIV, IAV and HDV.
Keywords: DSIF; HDV; HIV; IAV; NELF; RNA polymerase II; promoter-proximal pause.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Negative elongation factor is required for the maintenance of proviral latency but does not induce promoter-proximal pausing of RNA polymerase II on the HIV long terminal repeat.Mol Cell Biol. 2014 Jun;34(11):1911-28. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01013-13. Epub 2014 Mar 17. Mol Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24636995 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Regions in the Spt5 Subunit of DRB Sensitivity-inducing Factor (DSIF) That Are Involved in Promoter-proximal Pausing.J Biol Chem. 2017 Mar 31;292(13):5555-5570. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.760751. Epub 2017 Feb 17. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28213523 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions between DSIF (DRB sensitivity inducing factor), NELF (negative elongation factor), and the Drosophila RNA polymerase II transcription elongation complex.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Jun 22;107(25):11301-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1000681107. Epub 2010 Jun 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20534440 Free PMC article.
-
Pause Patrol: Negative Elongation Factor's Role in Promoter-Proximal Pausing and Beyond.J Mol Biol. 2025 Jan 1;437(1):168779. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2024.168779. Epub 2024 Sep 4. J Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39241983 Review.
-
Insight into Influenza: A Virus Cap-Snatching.Viruses. 2018 Nov 16;10(11):641. doi: 10.3390/v10110641. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 30453478 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Structural and functional characterization of the interaction between the influenza A virus RNA polymerase and the CTD of host RNA polymerase II.J Virol. 2024 May 14;98(5):e0013824. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00138-24. Epub 2024 Apr 2. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 38563748 Free PMC article.
-
PPM1G and its diagnostic, prognostic and therapeutic potential in HCC (Review).Int J Oncol. 2024 Nov;65(5):109. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2024.5697. Epub 2024 Sep 27. Int J Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39329206 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transactivation of the novel 5' cis-acting element of mouse mammary tumor virus (MMTV) by human retroviral transactivators Tat and Tax.Commun Biol. 2024 Nov 16;7(1):1521. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-07139-9. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 39550519 Free PMC article.
-
Virulence and transmission characteristics of clade 2.3.4.4b H5N6 subtype avian influenza viruses possessing different internal gene constellations.Virulence. 2023 Dec;14(1):2250065. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2023.2250065. Virulence. 2023. PMID: 37635408 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vermeulen M., Mulder K.W., Denissov S., Pijnappel W.W.M.P., van Schaik F.M.A., Varier R.A., Baltissen M.P.A., Stunnenberg H.G., Mann M., Timmers H.T.M. Selective Anchoring of TFIID to Nucleosomes by Trimethylation of Histone H3 Lysine 4. Cell. 2007;131:58–69. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.08.016. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

