Vaccination Decreases the Infectious Viral Load of Delta Variant SARS-CoV-2 in Asymptomatic Patients
- PMID: 36146877
- PMCID: PMC9503182
- DOI: 10.3390/v14092071
Vaccination Decreases the Infectious Viral Load of Delta Variant SARS-CoV-2 in Asymptomatic Patients
Abstract
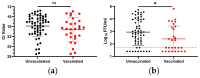
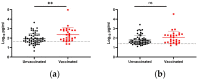
The Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2 has caused many breakthrough infections in fully vaccinated individuals. While vaccine status did not generally impact the number of viral RNA genome copies in nasopharyngeal swabs of breakthrough patients, as measured by Ct values, it has been previously found to decrease the infectious viral load in symptomatic patients. We quantified the viral RNA, infectious virus, and anti-spike IgA in nasopharyngeal swabs collected from individuals asymptomatically infected with the Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2. Vaccination decreased the infectious viral load, but not the amount of viral RNA. Furthermore, vaccinees with asymptomatic infections had significantly higher levels of anti-spike IgA in their nasal secretions compared to unvaccinated individuals with asymptomatic infections. Thus, vaccination may decrease the transmission risk of Delta, and perhaps other variants, despite not affecting the amount of viral RNA measured in nasopharyngeal swabs.
Keywords: B.1.617.2; COVID-19; IgA; SARS-CoV-2; breakthrough; delta; vaccination.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Does the COVID-19 Vaccination Reduce the Risk to Transmit SARS-CoV-2 to Others?Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1457:247-264. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-61939-7_14. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 39283431 Review.
-
Association of mRNA Vaccination With Clinical and Virologic Features of COVID-19 Among US Essential and Frontline Workers.JAMA. 2022 Oct 18;328(15):1523-1533. doi: 10.1001/jama.2022.18550. JAMA. 2022. PMID: 36255426 Free PMC article.
-
Community transmission and viral load kinetics of the SARS-CoV-2 delta (B.1.617.2) variant in vaccinated and unvaccinated individuals in the UK: a prospective, longitudinal, cohort study.Lancet Infect Dis. 2022 Feb;22(2):183-195. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00648-4. Epub 2021 Oct 29. Lancet Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 34756186 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of the Delta Variant and Vaccination on the SARS-CoV-2 Viral Load.Viruses. 2022 Feb 4;14(2):323. doi: 10.3390/v14020323. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35215916 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review of Vaccine Breakthrough Infections by SARS-CoV-2 Delta Variant.Int J Biol Sci. 2022 Jan 1;18(2):889-900. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.68973. eCollection 2022. Int J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35002532 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Does the COVID-19 Vaccination Reduce the Risk to Transmit SARS-CoV-2 to Others?Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1457:247-264. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-61939-7_14. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 39283431 Review.
-
The Effects of CoronaVac and ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 in Reducing Severe Illness in Thailand: A Retrospective Cohort Study.Trop Med Infect Dis. 2023 Jan 31;8(2):95. doi: 10.3390/tropicalmed8020095. Trop Med Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 36828511 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of infection severity of vaccinated and unvaccinated health workers with Corona Virus: A cohort study.J Educ Health Promot. 2023 Sep 29;12:336. doi: 10.4103/jehp.jehp_440_23. eCollection 2023. J Educ Health Promot. 2023. PMID: 38023101 Free PMC article.
-
Immunogenicity and efficacy of vaccine boosters against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron subvariant BA.5 in male Syrian hamsters.Nat Commun. 2023 Jul 17;14(1):4260. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-40033-2. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37460536 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thompson M.G., Burgess J.L., Naleway A.L., Tyner H.L., Yoon S.K., Meece J., Olsho L.E.W., Caban-Martinez A.J., Fowlkes A., Lutrick K., et al. Interim Estimates of Vaccine Effectiveness of BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273 COVID-19 Vaccines in Preventing SARS-CoV-2 Infection Among Health Care Personnel, First Responders, and Other Essential and Frontline Workers-Eight U.S. Locations, December 2020–March 2021. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2021;70:495–500. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brown C.M., Vostok J., Johnson H., Burns M., Gharpure R., Sami S., Sabo R.T., Hall N., Foreman A., Schubert P.L., et al. Outbreak of SARS-CoV-2 Infections, Including COVID-19 Vaccine Breakthrough Infections, Associated with Large Public Gatherings-Barnstable County, Massachusetts, July 2021. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2021;70:1059–1062. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7031e2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Levine-Tiefenbrun M., Yelin I., Alapi H., Katz R., Herzel E., Kuint J., Chodick G., Gazit S., Patalon T., Kishony R. Viral loads of Delta-variant SARS-CoV-2 breakthrough infections after vaccination and booster with BNT162b2. Nat. Med. 2021;27:2108–2110. doi: 10.1038/s41591-021-01575-4. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nielsen M.C., Machado R.R.G., Mitchell B.M., McConnell A.J., Saada N.I., Weaver S.C., Ren P. A Comparison of Seegene Technologies Novaplex SARS-CoV-2 Variants I, II, and IV Assays with Spike Gene Sequencing for Detection of Known Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Variants. J. Mol. Diagn. 2022;24:455–461. doi: 10.1016/j.jmoldx.2022.02.001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

