Antiviral Activity of Crude Polysaccharide Derived from Seaweed against IHNV and IPNV In Vitro
- PMID: 36146887
- PMCID: PMC9501831
- DOI: 10.3390/v14092080
Antiviral Activity of Crude Polysaccharide Derived from Seaweed against IHNV and IPNV In Vitro
Abstract
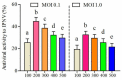
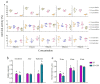
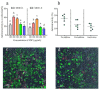
Both infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus (IHNV) and infectious pancreatic necrosis virus (IPNV) are the causative agents of acute and highly contagious diseases of juvenile salmonids, resulting in severe economic losses to these cold-water fish globally. There is an urgent need to explore antiviral agents against IHNV and IPNV due to the lack of commercially available vaccines and antiviral drugs. More importantly, the co-infection of IHNV and IPNV is prevalent in nature, which not only aggravates extensive damage to the salmonids but also poses challenges to its prevention and control. The antiviral effects of a crude polysaccharide derived from seaweed (CSP) on IHNV and IPNV were evaluated in this study separately. Furthermore, the underlying antiviral mechanisms of CSP to IHNV and IPNV were analyzed, respectively. The results showed that CSP possessed excellent safety and good ability to inhibit IHNV, IPNV, and their co-infection. CSP preferred to act at the early stage of viral infection. The antiviral mechanism of CSP on IHNV is possibly involved in preventing viral attachment and release, while in IPNV, it is involved in suppressing viral attachment, entry, and release. Taken together, the results of this study shed new light on developing novel agents against viral infection in salmonid fish.
Keywords: IHNV; IPNV; antivirus; co-infection; polysaccharide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Early or Simultaneous Infection with Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus Inhibits Infectious Hematopoietic Necrosis Virus Replication and Induces a Stronger Antiviral Response during Co-infection in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss).Viruses. 2022 Aug 6;14(8):1732. doi: 10.3390/v14081732. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 36016354 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a recombinant adenovirus-vectored vaccine against both infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus and infectious pancreatic necrosis virus in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss).Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023 Jan;132:108457. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2022.108457. Epub 2022 Nov 29. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36455780
-
Infectious pancreatic necrosis virus inhibits infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus at the early stage of infection in a time dependent manner during Co-infection in Chinook salmon embryo cell lines.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020 Jul;102:361-367. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2020.05.010. Epub 2020 May 6. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32387559
-
Immunization with viral antigens: infectious pancreatic necrosis.Dev Biol Stand. 1997;90:191-9. Dev Biol Stand. 1997. PMID: 9270848 Review.
-
Epidemiological characteristics of infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus (IHNV): a review.Vet Res. 2016 Jun 10;47(1):63. doi: 10.1186/s13567-016-0341-1. Vet Res. 2016. PMID: 27287024 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Extraction Optimization and Anti-Tumor Activity of Polysaccharides from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii.Mar Drugs. 2024 Aug 2;22(8):356. doi: 10.3390/md22080356. Mar Drugs. 2024. PMID: 39195472 Free PMC article.
-
Kaempferol is a novel antiviral agent against channel catfish virus infection through blocking viral attachment and penetration in vitro.Front Vet Sci. 2023 Dec 4;10:1323646. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1323646. eCollection 2023. Front Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 38111732 Free PMC article.
-
Portulaca oleracea L. Polysaccharide Inhibits Porcine Rotavirus In Vitro.Animals (Basel). 2023 Jul 14;13(14):2306. doi: 10.3390/ani13142306. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37508085 Free PMC article.
References
-
- OIE World Organization for Animal Health, Aquatic Animal Health Code. [(accessed on 12 October 2018)]. Available online: http://www.oie.int/international-standardsetting/aquatic-code/access-online.
-
- Alonso M., Rodriguez Saint-Jean S., Perez-Prieto S.I. Virulence of infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus and infectious pancreatic necrosis virus coinfection in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and nucleotide sequence analysis of the IHNV glycoprotein gene. Arch. Virol. 2003;148:1507–1521. doi: 10.1007/s00705-003-0116-7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rucker R.R., Whippie W.J., Parvin J.R. A contagious disease of salmon possibly of virus origin, US Fish Wildl. Serv. Fish Bull. 1953;54:174–175.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

