Perioperative management of the thyrotoxic patients: A systematic review
- PMID: 36147169
- PMCID: PMC9486717
- DOI: 10.1016/j.amsu.2022.104487
Perioperative management of the thyrotoxic patients: A systematic review
Abstract
Background: Thyrotoxicosis is a clinical syndrome produced by a multitude of disorders. Thyrotoxicosis is a serious medical condition that, if left untreated, can lead to a fatal illness. This review of recent evidences give additional input for perioperative management of thyrotoxic patients.
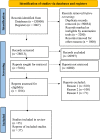
Methods: The literatures were found with Boolean operators in the form of thyrotoxicosis AND anesthesia, antithyroid medications AND perioperative optimization AND beta blockers OR calcium channel blockers in electronic data base sources such as the Cochrane library, PubMed, and Google scholar. This review was carried out in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) 2020 statement.
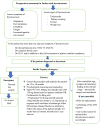
Conclusions: and recommendations: Before surgery and anesthesia, manifestation of thyrotoxicosis including palpitation, irritability etc should be ruled out.
Keywords: Management; Medications; Perioperative; Thyroid function tests; Thyrotoxicosis.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Risk stratification, prevention and management of perioperative corneal abrasion for non-ocular surgery: Systematic Review.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2023 Dec 4;86(1):373-381. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000001566. eCollection 2024 Jan. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2023. PMID: 38222698 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anesthetic Considerations and Perioperative Management of Spinal Cord Stimulators: Literature Review and Initial Recommendations.Pain Physician. 2017 May;20(4):319-329. Pain Physician. 2017. PMID: 28535554 Review.
-
Perioperative management of the thyrotoxic patient.Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2003 Jun;32(2):519-34. doi: 10.1016/s0889-8529(03)00010-0. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2003. PMID: 12800544 Review.
-
Comparing the Incidence of Propranolol and Esmolol-Related Cardiac Arrest in Patients With Thyroid Storm: A Systematic Literature Review.Cureus. 2023 Sep 4;15(9):e44655. doi: 10.7759/cureus.44655. eCollection 2023 Sep. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37799246 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation and Management of Children with Thyrotoxicosis.Recent Pat Endocr Metab Immune Drug Discov. 2017;11(1):22-31. doi: 10.2174/1872214812666180327112540. Recent Pat Endocr Metab Immune Drug Discov. 2017. PMID: 29589552 Review.
Cited by
-
Perioperative Care of a Child With Hyperthyroidism.J Med Cases. 2024 Apr;15(2-3):49-54. doi: 10.14740/jmc4197. Epub 2024 Apr 8. J Med Cases. 2024. PMID: 38646421 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the impact of short-term Lugol's solution on toxic nodular thyroid disease: a pre-post-intervention study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Jul 25;15:1420154. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1420154. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39119004 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Perioperative Implications in a Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Patient Undergoing Endonasal Orbital Decompression: A Case Report.Cureus. 2024 Aug 18;16(8):e67115. doi: 10.7759/cureus.67115. eCollection 2024 Aug. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39290945 Free PMC article.
-
Thyroid storm during the recovery phase after non-thyroid surgery in a hyperthyroid patient: a case report and literature review.Front Surg. 2025 Jul 14;12:1633314. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2025.1633314. eCollection 2025. Front Surg. 2025. PMID: 40726736 Free PMC article.
-
Total Thyroidectomy while on Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for Thyroid Storm.Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2024 Apr;76(2):2108-2112. doi: 10.1007/s12070-023-04430-9. Epub 2023 Dec 27. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2024. PMID: 38566716 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sharma A., Stan M.N. Thyrotoxicosis: diagnosis and management. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2019;94(6):1048–1064. - PubMed
-
- Ross D.S., Burch H.B., Cooper D.S., Greenlee M.C., Laurberg P., Maia A.L., et al. 2016 American Thyroid Association guidelines for diagnosis and management of hyperthyroidism and other causes of thyrotoxicosis. Thyroid. 2016;26(10):1343–1421. - PubMed
-
- Łacka K., Fraczek M.M. [Classification and etiology of hyperthyroidism]. Polski merkuriusz lekarski : organ Polskiego. Tow. Lekarskiego. 2014;36(213):206–211. - PubMed
-
- Taylor P.N., Albrecht D., Scholz A., Gutierrez-Buey G., Lazarus J.H., Dayan C.M., et al. Global epidemiology of hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018;14(5):301–316. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

