Detection of Vascular Inflammation and Oxidative Stress by Cotinine in Smokers: Measured Through Interleukin-6 and Superoxide Dismutase
- PMID: 36147199
- PMCID: PMC9489220
- DOI: 10.2147/IJGM.S367125
Detection of Vascular Inflammation and Oxidative Stress by Cotinine in Smokers: Measured Through Interleukin-6 and Superoxide Dismutase
Abstract
Purpose: Smoking is a significant risk factor in developing cardiovascular disease pathogenesis through oxidative stress and inflammation mechanisms. This study used cotinine as a biomarker of nicotine exposure levels in the body, which was associated with levels of Interleukin-6 (IL-6) and Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) as markers of oxidative stress and vascular inflammation. The research aimed to analyze the effect of cotinine levels on the expression of IL-6 and SOD.
Methods: This study used a cross-sectional design on 200 subjects, consisting 100 smokers and 100 non-smokers. Cotinine levels, IL-6 expression, and SOD were measured from the blood serum of each subject using the Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) method. Then the data were analyzed using Generalized Structured Component Analysis (GSCA).
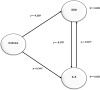
Results: There was a significant effect of cotinine levels on the reduction of SOD mediated by IL-6 (CR = 4.006). Cotinine levels also increased IL-6 mediated by SOD (CR = 4.292). The structural model shows that higher cotinine levels will increase IL-6 expression, and conversely, SOD expression will decrease.
Conclusion: High cotinine levels cause an increase in the inflammatory process and oxidative stress in the vasculature of smokers, which is characterized by high IL-6 expression and low SOD expression.
Keywords: IL-6; SOD; cardiovascular disease; cotinine; oxidative stress; smoking.
© 2022 Kumboyono et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization.Cardiovascular Diseases (Cvds): Key Facts. World Health Organization; 2021. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases...). Accessed September 8, 2022.
-
- Brunssen C, Giebe S, Hofmann A, Brux M, Morawietz H. Evaluation of cytotoxic, oxidative, and pro-inflammatory effects of aqueous cigarette smoke extract on human monocytes: a potential model system for assessment of next-generation tobacco and nicotine products. Applied Vitro Toxicol. 2017;3(1):121–130. doi:10.1089/aivt.2016.0037 - DOI
-
- Kundu J, Kundu S. Cardiovascular disease (CVD) and its associated risk factors among older adults in India: evidence from LASI Wave 1. Clin Epidemiol Global Health. 2022;13:100937. doi:10.1016/j.cegh.2021.100937 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical