Combined transcriptomic and metabolomic analysis reveals a role for adenosine triphosphate-binding cassette transporters and cell wall remodeling in response to salt stress in strawberry
- PMID: 36147238
- PMCID: PMC9486094
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.996765
Combined transcriptomic and metabolomic analysis reveals a role for adenosine triphosphate-binding cassette transporters and cell wall remodeling in response to salt stress in strawberry
Abstract
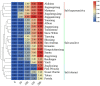
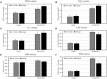
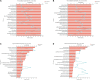
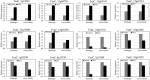
Strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa Duch) are sensitive to salt stress, and breeding salt-tolerant strawberry cultivars is the primary method to develop resistance to increased soil salinization. However, the underlying molecular mechanisms mediating the response of strawberry to salinity stress remain largely unknown. This study evaluated the salinity tolerance of 24 strawberry varieties, and transcriptomic and metabolomic analysis were performed of 'Sweet Charlie' (salt-tolerant) and 'Benihoppe' (salt-sensitive) to explore salt tolerance mechanisms in strawberry. Compared with the control, we identified 3412 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) and 209 differentially accumulated metabolites (DAMs) in 'Benihoppe,' and 5102 DEGs and 230 DAMs in 'Sweet Charlie.' DEGs Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment analyses indicated that the DEGs in 'Benihoppe' were enriched for ion homeostasis related terms, while in 'Sweet Charlie,' terms related to cell wall remodeling were over-represented. DEGs related to ion homeostasis and cell wall remodeling exhibited differential expression patterns in 'Benihoppe' and 'Sweet Charlie.' In 'Benihoppe,' 21 ion homeostasis-related DEGs and 32 cell wall remodeling-related DEGs were upregulated, while 23 ion homeostasis-related DEGs and 138 cell wall remodeling-related DEGs were downregulated. In 'Sweet Charlie,' 72 ion homeostasis-related DEGs and 275 cell wall remodeling-related DEGs were upregulated, while 11 ion homeostasis-related DEGs and 20 cell wall remodeling-related DEGs were downregulated. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway analyses showed only four KEGG enriched pathways were shared between 'Benihoppe' and 'Sweet Charlie,' including flavonoid biosynthesis, phenylalanine metabolism, phenylpropanoid biosynthesis and ubiquinone, and other terpenoid-quinone biosynthesis. Integrating the results of transcriptomic and metabolomics analyses showed that adenosine triphosphate-binding cassette (ABC) transporters and flavonoid pathway genes might play important roles in the salt stress response in strawberry, and DAMs and DEGs related to ABC transporter and flavonoid pathways were differentially expressed or accumulated. The results of this study reveal that cell wall remodeling and ABC transporters contribute to the response to salt stress in strawberry, and that related genes showed differential expression patterns in varieties with different salt tolerances. These findings provide new insights into the underlying molecular mechanism of strawberry response to salt stress and suggest potential targets for the breeding of salt-tolerant strawberry varieties.
Keywords: ABC transporter; cell wall remodeling; salinity tolerance; salt stress; strawberry.
Copyright © 2022 Li, Chang, Sun, Dong, Zhong, Gao, Zhang, Wei, Wei, Zhang, Wang and Sun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Combined full-length transcriptomic and metabolomic analysis reveals the regulatory mechanisms of adaptation to salt stress in asparagus.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Oct 27;13:1050840. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1050840. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36388563 Free PMC article.
-
Combined transcriptomic and metabolomic analysis revealed the salt tolerance mechanism of Populus talassica × Populus euphratica.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Mar 20;25(1):361. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06288-1. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 40114044 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated transcriptomic and metabolomic analyses provide insights into defense against Colletotrichum fructicola in octoploid strawberries.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Feb 13;25(1):190. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06057-0. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 39948459 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic Analysis of Betula halophila in Response to Salt Stress.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Oct 31;19(11):3412. doi: 10.3390/ijms19113412. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30384437 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome analysis and differential gene expression profiling of two contrasting quinoa genotypes in response to salt stress.BMC Plant Biol. 2020 Dec 30;20(1):568. doi: 10.1186/s12870-020-02753-1. BMC Plant Biol. 2020. PMID: 33380327 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Integrated metabolomic and transcriptomic analysis reveals the role of phenylpropanoid biosynthesis pathway in tomato roots during salt stress.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Dec 8;13:1023696. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1023696. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36570882 Free PMC article.
-
Combined full-length transcriptomic and metabolomic analysis reveals the regulatory mechanisms of adaptation to salt stress in asparagus.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Oct 27;13:1050840. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1050840. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36388563 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification, characterization, and functional analysis of the CHX, SOS, and RLK genes in Solanum lycopersicum under salt stress.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 7;15(1):1142. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-83221-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39774029 Free PMC article.
-
Combined transcriptomic and metabolomic analysis revealed the salt tolerance mechanism of Populus talassica × Populus euphratica.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Mar 20;25(1):361. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06288-1. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 40114044 Free PMC article.
-
Exogenous nano-silicon enhances the ability of intercropped faba bean to alleviate cadmium toxicity and resist Fusarium wilt.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 Apr 1;23(1):262. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03330-0. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40170068 Free PMC article.
References
-
- An P., Li X., Zheng Y., Matsuura A., Abe J., Eneji A. E., et al. (2014). Effects of NaCl on root growth and cell wall composition of two soya bean cultivars with contrasting salt tolerance. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 200 212–218. 10.1111/jac.12060 - DOI
-
- Bharti P., Mahajan M., Vishwakarma A. K., Bhardwaj J., Yadav S. K. (2015). AtROS1 overexpression provides evidence for epigenetic regulation of genes encoding enzymes of flavonoid biosynthesis and antioxidant pathways during salt stress in transgenic tobacco. J. Exp. Bot. 66 5959–5969. 10.1093/jxb/erv304 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

