INVESTIGATING THE EFFECT OF TAU DEPOSITION AND APOE ON HIPPOCAMPAL MORPHOMETRY IN ALZHEIMER'S DISEASE: A FEDERATED CHOW TEST MODEL
- PMID: 36147309
- PMCID: PMC9491515
- DOI: 10.1109/isbi52829.2022.9761576
INVESTIGATING THE EFFECT OF TAU DEPOSITION AND APOE ON HIPPOCAMPAL MORPHOMETRY IN ALZHEIMER'S DISEASE: A FEDERATED CHOW TEST MODEL
Abstract
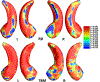
Alzheimer's disease (AD) affects more than 1 in 9 people age 65 and older and becomes an urgent public health concern as the global population ages. Tau tangle is the specific protein pathological hallmark of AD and plays a crucial role in leading to dementia-related structural deformations observed in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans. The volume loss of hippocampus is mainly related to the development of AD. Besides, apolipoprotein E (APOE) also has significant effects on the risk of developing AD. However, few studies focus on integrating genotypes, MRI, and tau deposition to infer multimodal relationships. In this paper, we proposed a federated chow test model to study the synergistic effects of APOE and tau on hippocampal morphometry. Our experimental results demonstrate our model can detect the difference of tau deposition and hippocampal atrophy among the cohorts with different genotypes and subiculum and cornu ammonis 1 (CA1 subfield) were identified as hippocampal subregions where atrophy is strongly associated with abnormal tau in the homozygote cohort. Our model will provide novel insight into the neural mechanisms about the individual impact of APOE and tau deposition on brain imaging.
Keywords: APOE; Alzheimer’s Disease; Hippocampal Morphometry; federated chow test; tau deposition.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A Surface-Based Federated Chow Test Model for Integrating APOE Status, Tau Deposition Measure, and Hippocampal Surface Morphometry.J Alzheimers Dis. 2023;93(3):1153-1168. doi: 10.3233/JAD-230034. J Alzheimers Dis. 2023. PMID: 37182882 Free PMC article.
-
Federated Morphometry Feature Selection for Hippocampal Morphometry Associated Beta-Amyloid and Tau Pathology.Front Neurosci. 2021 Nov 25;15:762458. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.762458. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34899166 Free PMC article.
-
Earliest amyloid and tau deposition modulate the influence of limbic networks during closed-loop hippocampal downregulation.Brain. 2020 Mar 1;143(3):976-992. doi: 10.1093/brain/awaa011. Brain. 2020. PMID: 32091109 Free PMC article.
-
The APOE ε4 variant and hippocampal atrophy in Alzheimer's disease and Lewy body dementia: a systematic review of magnetic resonance imaging studies and therapeutic relevance.Expert Rev Neurother. 2021 Aug;21(8):851-870. doi: 10.1080/14737175.2021.1956904. Epub 2021 Aug 13. Expert Rev Neurother. 2021. PMID: 34311631
-
Potential predictors of hippocampal atrophy in Alzheimer's disease.Drugs Aging. 2011 Jan 1;28(1):1-11. doi: 10.2165/11586390-000000000-00000. Drugs Aging. 2011. PMID: 21174483 Review.
Cited by
-
Hippocampal subfields: volume, neuropathological vulnerability and cognitive decline in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2025 May 30;17(1):121. doi: 10.1186/s13195-025-01768-w. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40448161 Free PMC article.
-
Which neuroimaging and fluid biomarkers method is better in theranostic of Alzheimer's disease? An umbrella review.IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2024 Feb 29;16:403-417. doi: 10.1016/j.ibneur.2024.02.007. eCollection 2024 Jun. IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38497046 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
