Integrated transcriptomics and metabolomics analysis of the hippocampus reveals altered neuroinflammation, downregulated metabolism and synapse in sepsis-associated encephalopathy
- PMID: 36147346
- PMCID: PMC9486403
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1004745
Integrated transcriptomics and metabolomics analysis of the hippocampus reveals altered neuroinflammation, downregulated metabolism and synapse in sepsis-associated encephalopathy
Abstract
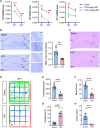
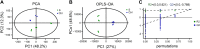
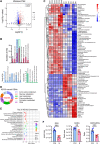
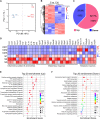
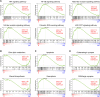
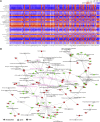
Sepsis-associated encephalopathy (SAE) is an intricated complication of sepsis that brings abnormal emotional and memory dysfunction and increases patients' mortality. Patients' alterations and abnormal function seen in SAE occur in the hippocampus, the primary brain region responsible for memory and emotional control, but the underlying pathophysiological mechanisms remain unclear. In the current study, we employed an integrative analysis combining the RNA-seq-based transcriptomics and liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry (LC-MS)-based metabolomics to comprehensively obtain the enriched genes and metabolites and their core network pathways in the endotoxin (LPS)-injected SAE mice model. As a result, SAE mice exhibited behavioral changes, and their hippocampus showed upregulated inflammatory cytokines and morphological alterations. The omics analysis identified 81 differentially expressed metabolites (variable importance in projection [VIP] > 1 and p < 0.05) and 1747 differentially expressed genes (Foldchange >2 and p < 0.05) were detected in SAE-grouped hippocampus. Moreover, 31 compounds and 100 potential target genes were employed for the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) Markup Language (KGML) network analysis to explore the core signaling pathways for the progression of SAE. The integrative pathway analysis showed that various dysregulated metabolism pathways, including lipids metabolism, amino acids, glucose and nucleotides, inflammation-related pathways, and deregulated synapses, were tightly associated with hippocampus dysfunction at early SAE. These findings provide a landscape for understanding the pathophysiological mechanisms of the hippocampus in the progression of SAE and pave the way to identify therapeutic targets in future studies.
Keywords: RNA sequencing; integrative analysis; metabolomics; multi-omics analysis; neuroinflammation; sepsis-associated encephalopathy.
Copyright © 2022 Xu, Li, Zhang, Le, Huang, Fu, Croppi, Qian, Zhang, Zhang and Lu.
Conflict of interest statement
Author GC is employed by Connect Biopharma Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Anders S., Huber W. (2012). Differential expression of RNA-Seq data at the gene level - the DESeq package[J]. Heidelberg,Germany: European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

