Tumor Microenvironment and its Implications for Antitumor Immunity in Cholangiocarcinoma: Future Perspectives for Novel Therapies
- PMID: 36147461
- PMCID: PMC9461676
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.73949
Tumor Microenvironment and its Implications for Antitumor Immunity in Cholangiocarcinoma: Future Perspectives for Novel Therapies
Abstract
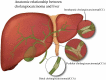
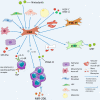
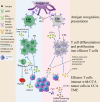
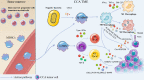
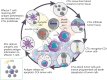
The incidence of cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) has been increasing over the past few years. Although there are surgery, chemotherapy and other conventional treatment methods, the effect is not as expected. At present, immunotherapy has become the research frontier of cancer treatment, and CCA tumor microenvironment (TME) is becoming a hot exploration direction of immunobiology. TME can affect tumor progression through changes in metabolism, secretion and immunity. Accordingly, understanding the role played by immune cells and stromal cells in TME is important for the study of CCA immunotherapy. This review will discuss the interactions between immune cells (including CD8+ T cells, CD4+ T cells, macrophages, natural killer cells, dendritic cells, myeloid suppressor cells, mast cells, and neutrophils) and stromal cells (including cancer-associated fibroblasts, endothelial cells) in the TME of CCA. In addition, we will also discuss current research results on TME of CCA and recent advances in immunotherapy.
Keywords: cholangiocarcinoma; immune mechanism; immunotherapy; prognostic markers; targeted therapy; tumor microenvironment.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

References
-
- Benson AB, D'Angelica MI, Abbott DE, Anaya DA, Anders R, Are C. et al. Hepatobiliary Cancers, Version 2.2021, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2021;19:541–65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

