Non-coding RNAs in diabetes mellitus and diabetic cardiovascular disease
- PMID: 36147580
- PMCID: PMC9487522
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.961802
Non-coding RNAs in diabetes mellitus and diabetic cardiovascular disease
Abstract
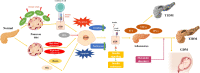
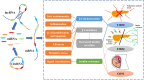
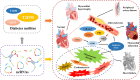
More than 10% of the world's population already suffers from varying degrees of diabetes mellitus (DM), but there is still no cure for the disease. Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is one of the most common and dangerous of the many health complications that can be brought on by DM, and has become the leading cause of death in people with diabetes. While research on DM and associated CVD is advancing, the specific mechanisms of their development are still unclear. Given the threat of DM and CVD to humans, the search for new predictive markers and therapeutic ideas is imminent. Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) have been a popular subject of research in recent years. Although they do not encode proteins, they play an important role in living organisms, and they can cause disease when their expression is abnormal. Numerous studies have observed aberrant ncRNAs in patients with DM complications, suggesting that they may play an important role in the development of DM and CVD and could potentially act as biomarkers for diagnosis. There is additional evidence that treatment with existing drugs for DM, such as metformin, alters ncRNA expression levels, suggesting that regulation of ncRNA expression may be a key mechanism in future DM treatment. In this review, we assess the role of ncRNAs in the development of DM and CVD, as well as the evidence for ncRNAs as potential therapeutic targets, and make use of bioinformatics to analyze differential ncRNAs with potential functions in DM.
Keywords: cardiovascular disease; circular RNA; diabetes mellitus; long non-coding RNA; microRNA.
Copyright © 2022 Li, Wang, Jiang, Gao, Sun, Li, Chen, Lin and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Non-coding RNAs regulating mitochondrial function in cardiovascular diseases.J Mol Med (Berl). 2023 May;101(5):501-526. doi: 10.1007/s00109-023-02305-8. Epub 2023 Apr 4. J Mol Med (Berl). 2023. PMID: 37014377 Review.
-
Noncoding RNAs as therapeutic targets in atherosclerosis with diabetes mellitus.Cardiovasc Ther. 2018 Aug;36(4):e12436. doi: 10.1111/1755-5922.12436. Epub 2018 Jun 28. Cardiovasc Ther. 2018. PMID: 29797660 Review.
-
circRNAs Signature as Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker for Diabetes Mellitus and Related Cardiovascular Complications.Cells. 2020 Mar 9;9(3):659. doi: 10.3390/cells9030659. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32182790 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of non-coding RNAs in diabetes-induced osteoporosis.Differentiation. 2023 Sep-Oct;133:98-108. doi: 10.1016/j.diff.2023.08.002. Epub 2023 Aug 22. Differentiation. 2023. PMID: 37643534 Review.
-
Systematic review regulatory principles of non-coding RNAs in cardiovascular diseases.Brief Bioinform. 2019 Jan 18;20(1):66-76. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbx095. Brief Bioinform. 2019. PMID: 28968629
Cited by
-
Gene expression analysis reveals diabetes-related gene signatures.Hum Genomics. 2024 Feb 8;18(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s40246-024-00582-z. Hum Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38326874 Free PMC article.
-
The role of ncRNA regulatory mechanisms in diseases-case on gestational diabetes.Brief Bioinform. 2023 Nov 22;25(1):bbad489. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbad489. Brief Bioinform. 2023. PMID: 38189542 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Processes Involved in the Shared Pathways between Cardiovascular Diseases and Diabetes.Biomedicines. 2023 Sep 23;11(10):2611. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11102611. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37892985 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small dense low density lipoprotein predominance in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus using Mendelian randomization.PLoS One. 2024 Feb 8;19(2):e0298070. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0298070. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38330008 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of lncRNAs in brain development and pathogenesis: Emerging therapeutic opportunities.Mol Ther. 2023 Jun 7;31(6):1550-1561. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2023.02.008. Epub 2023 Feb 14. Mol Ther. 2023. PMID: 36793211 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

