Immunometabolism of macrophages regulates skeletal muscle regeneration
- PMID: 36147742
- PMCID: PMC9485946
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2022.948819
Immunometabolism of macrophages regulates skeletal muscle regeneration
Abstract
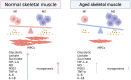
Sarcopenia is an age-related progressive loss of skeletal muscle mass, quality, and strength disease. In addition, sarcopenia is tightly correlated with age-associated pathologies, such as sarcopenic obesity and osteoporosis. Further understanding of disease mechanisms and the therapeutic strategies in muscle regeneration requires a deeper knowledge of the interaction of skeletal muscle and other cells in the muscle tissue. Skeletal muscle regeneration is a complex process that requires a series of highly coordinated events involving communication between muscle stem cells and niche cells, such as muscle fibro/adipogenic progenitors and macrophages. Macrophages play a critical role in tissue regeneration and the maintenance of muscle homeostasis by producing growth factors and cytokines that regulate muscle stem cells and myofibroblast activation. Furthermore, the aging-related immune dysregulation associated with the release of trophic factors and the polarization in macrophages transiently affect the inflammatory phase and impair muscle regeneration. In this review, we focus on the role and regulation of macrophages in skeletal muscle regeneration and homeostasis. The aim of this review is to highlight the important roles of macrophages as a therapeutic target in age-related sarcopenia and the increasing understanding of how macrophages are regulated will help to advance skeletal muscle regeneration.
Keywords: macrophages; metabolism; muscle regeneration; muscle stem cells; sarcopenia.
Copyright © 2022 Chen, Lee, Wu, Lin and Lee.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Alamdari N., Constantin-Teodosiu D., Murton A. J., Gardiner S. M., Bennett T., Layfield R., et al. (2008). Temporal changes in the involvement of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex in muscle lactate accumulation during lipopolysaccharide infusion in rats. J. Physiol. 586, 1767–1775. 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.149625 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

