Characterization of cellular senescence in aging skeletal muscle
- PMID: 36147777
- PMCID: PMC9491365
- DOI: 10.1038/s43587-022-00250-8
Characterization of cellular senescence in aging skeletal muscle
Abstract
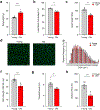
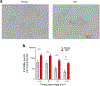
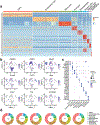
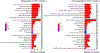
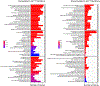
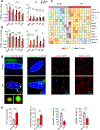
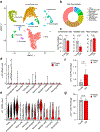
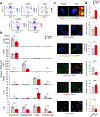
Senescence is a cell fate that contributes to multiple aging-related pathologies. Despite profound age-associated changes in skeletal muscle (SkM), whether its constituent cells are prone to senesce has not been methodically examined. Herein, using single cell and bulk RNA-sequencing and complementary imaging methods on SkM of young and old mice, we demonstrate that a subpopulation of old fibroadipogenic progenitors highly expresses p16 Ink4a together with multiple senescence-related genes and, concomitantly, exhibits DNA damage and chromatin reorganization. Through analysis of isolated myofibers, we also detail a senescence phenotype within a subset of old cells, governed instead by p2 Cip1 . Administration of a senotherapeutic intervention to old mice countered age-related molecular and morphological changes and improved SkM strength. Finally, we found that the senescence phenotype is conserved in SkM from older humans. Collectively, our data provide compelling evidence for cellular senescence as a hallmark and potentially tractable mediator of SkM aging.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01477164.
Figures

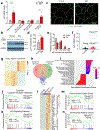
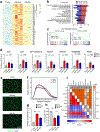
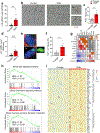
Comment in
-
Senescence diversity in muscle aging.Nat Aging. 2022 Jul;2(7):570-572. doi: 10.1038/s43587-022-00255-3. Nat Aging. 2022. PMID: 37117776 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- T32 AG049672/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG031679/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- R01 AG055529/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AR056950/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R00 AG058798/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AG060907/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 CA268103/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K99 AG058798/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 CA268103/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG062413/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG068048/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK084567/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

