Mechanisms of Zhenwu decoction for the treatment of renal fibrosis at various stages: What is the role of Corynebacterium?
- PMID: 36147851
- PMCID: PMC9485941
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.913465
Mechanisms of Zhenwu decoction for the treatment of renal fibrosis at various stages: What is the role of Corynebacterium?
Abstract
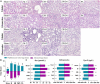
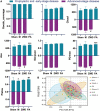
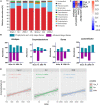
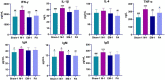
Many studies demonstrated that Zhenwu decoction (ZWD) is effective in the treatment of kidney fibrosis, whereas the mechanism remains unclear. In this work, a microbiomics-based strategy was used to investigate the mechanism of protective effects of ZWD on kidney fibrosis. Unilateral ureteral obstruction was used to replicate a rat model of renal fibrosis, and rats were divided into prophylactic, early, and progression stages according to the timing of administration. Feces was collected to perform microbiota evaluation by high-throughput 16S DNA sequencing. The results indicated that Corynebacterium, Alistipes, Dorea, and Lactonifactor were highlighted as key targeted flora of ZWD in the treatment of renal fibrosis, and their biological functions were related to inflammation, immunity, and renal excretion. Especially, Corynebacterium presented a significant positive correlation with the concentration of Cys-C, Scr, and BUN. The studies on the changes in inflammatory cytokines (INF-γ, IL-1β, IL-4, and TNF-α) and immunoglobulin (IgA, IgM, and IgG) confirmed the beneficial effects of ZWD on kidney fibrosis. Therefore, this study confirmed the protective effect of ZWD against renal fibrosis at various disease stages, and its mechanism was associated with re-establishing dysbiosis of the intestinal microbiota, reducing inflammation, as well as regulating immune functions. In particular, Corynebacterium may be a key flora in the treatment of renal fibrosis.
Keywords: Corynebacterium; Zhenwu decoction; inflammatory; intestinal microbiota; renal fibrosis.
Copyright © 2022 Du, Zhang, Ji, Wang, Zhao, Yan, Xiao and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mechanism of Zhenwu Decoction modulating TLR4/NF-κB/HIF-1α loop through miR-451 to delay renal fibrosis in type 2 CRS.Phytomedicine. 2024 Sep;132:155632. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155632. Epub 2024 May 22. Phytomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38851985
-
Integrating Network Pharmacology and an Experimental Model to Investigate the Effect of Zhenwu Decoction on Doxorubicin-Induced Heart Failure.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2023;26(14):2502-2516. doi: 10.2174/1386207326666230413091715. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2023. PMID: 37056062
-
Zhen Wu decoction represses renal fibrosis by invigorating tubular NRF2 and TFAM to fuel mitochondrial bioenergetics.Phytomedicine. 2023 Jan;108:154495. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154495. Epub 2022 Oct 8. Phytomedicine. 2023. PMID: 36257219
-
Renoprotective effect of Zhenwu decoction against renal fibrosis by regulation of oxidative damage and energy metabolism disorder.Sci Rep. 2018 Oct 2;8(1):14627. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-32115-9. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30279506 Free PMC article.
-
Urinary biomarkers in hydronephrosis.Dan Med J. 2013 Feb;60(2):B4582. Dan Med J. 2013. PMID: 23461995 Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in the study of key cells and signaling pathways in renal fibrosis and the interventional role of Chinese medicines.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Dec 2;15:1403227. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1403227. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39687302 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microbial Fermentation Enhances the Effect of Black Tea on Hyperlipidemia by Mediating Bile Acid Metabolism and Remodeling Intestinal Microbes.Nutrients. 2024 Mar 28;16(7):998. doi: 10.3390/nu16070998. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38613030 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

