Deep eutectic solvent-assisted fabrication of zirconium phytate thin nanosheets for important biomass transformations
- PMID: 36147961
- PMCID: PMC9485070
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.105039
Deep eutectic solvent-assisted fabrication of zirconium phytate thin nanosheets for important biomass transformations
Abstract
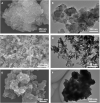
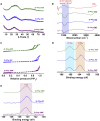
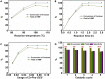
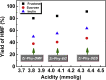
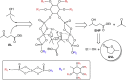
Utilization of naturally occurring resources to construct functional catalytic materials is significantly important, and facile and environmental-benign strategies are highly desired to afford the materials having a specific structure and good catalytic activity. Herein, we reported an innovative deep eutectic solvent (DES)-assisted strategy to synthesize zirconium phytate with a thin nanosheet structure (denoted as Zr-Phy-DES) using plant-originated phytic acid (PhyA) as the renewable building block. This strategy was eco-friendly and adjustable owing to the designability of DESs. The Zr-Phy-DES as an acidic catalyst showed high activity on two important biomass transformations, i.e., dehydration of carbohydrates and Meerwein-Ponndorf-Verley reduction of ethyl levulinate. Interestingly, Zr-Phy-DES showed higher catalytic performance than the zirconium phytates prepared in ethylene glycol and N,N-dimethylformamide, confirming the advantage of DESs for preparing functional materials. Notably, the unique feature of this proposed strategy is that renewable catalysts are prepared in an environmental-benign solvent for efficiently catalyzing biomass transformation.
Keywords: chemistry; green chemistry; materials chemistry; materials science; organic chemistry.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Porous Zirconium-Phytic Acid Hybrid: a Highly Efficient Catalyst for Meerwein-Ponndorf-Verley Reductions.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2015 Aug 3;54(32):9399-403. doi: 10.1002/anie.201504001. Epub 2015 Jul 14. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2015. PMID: 26177726
-
Recyclable Zr/Hf-Containing Acid-Base Bifunctional Catalysts for Hydrogen Transfer Upgrading of Biofuranics: A Review.Front Chem. 2021 Dec 21;9:812331. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2021.812331. eCollection 2021. Front Chem. 2021. PMID: 34993179 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fast Assembly of Metal Organic Framework UiO-66 in Acid-Base Tunable Deep Eutectic Solvent for the Acetalization of Benzaldehyde and Methanol.Molecules. 2022 Oct 25;27(21):7246. doi: 10.3390/molecules27217246. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36364073 Free PMC article.
-
Highly Efficient Transfer Hydrogenation of Biomass-Derived Furfural to Furfuryl Alcohol over Mesoporous Zr-Containing Hybrids with 5-Sulfosalicylic Acid as a Ligand.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Jul 28;19(15):9221. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19159221. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35954579 Free PMC article.
-
Advances of Ionic Liquids and Deep Eutectic Solvents in Green Processes of Biomass-Derived 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural.ChemSusChem. 2022 Jul 7;15(13):e202102635. doi: 10.1002/cssc.202102635. Epub 2022 Feb 10. ChemSusChem. 2022. PMID: 35088547 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring carbohydrate extraction from biomass using deep eutectic solvents: Factors and mechanisms.iScience. 2023 Aug 19;26(9):107671. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107671. eCollection 2023 Sep 15. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37680471 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abdelkader A.M., Kinloch I.A. Mechanochemical exfoliation of 2D crystals in deep eutectic solvents. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2016;4:4465–4472. doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.6b01195. - DOI
-
- Chen B., He C., Cao M., Qiu X., Ouyang X., Qian Y. Fabricating nickel phyllosilicate-like nanosheets to prepare a defect-rich catalyst for the one-pot conversion of lignin into hydrocarbons under mild conditions. Green Chem. 2022;24:846–857. doi: 10.1039/d1gc03909a. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

