Multifocal Neuroarthropathy of the Knee and Foot Induced by Physical Training of the Lower Extremities in a Patient With Latent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults
- PMID: 36148208
- PMCID: PMC9482758
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.28163
Multifocal Neuroarthropathy of the Knee and Foot Induced by Physical Training of the Lower Extremities in a Patient With Latent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults
Abstract
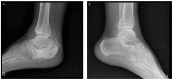
Charcot neuroarthropathy is a progressive arthropathy associated with neuropathy. In patients with diabetes, Charcot neuroarthropathy mostly affects the foot. In the present case, we encountered a rare presentation of Charcot neuroarthropathy of the knee and foot in a patient with latent autoimmune diabetes in adults. The patient, who may have developed the disease as a result of inappropriate physical exercise, was treated with total knee arthroplasty.
Keywords: charcot knee; diabetic polyneuropathy; latent autoimmune diabetes; neuroarthropathy; physical training; total knee arthroplasty.
Copyright © 2022, Kojima et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared financial relationships, which are detailed in the next section.
Figures


References
-
- Current concepts underlying the pathophysiology of acute Charcot neuroarthropathy in the diabetic foot and ankle. Yates TH, Cooperman SR, Shofler D, Agrawal DK. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2020;16:839–845. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
