Comparison of 3 Rates for the Continuous Infusion of Mivacurium During Ambulatory Vitreoretinal Surgery Under General Anesthesia: A Prospective, Randomized, Controlled Clinical Trial
- PMID: 36148320
- PMCID: PMC9489221
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S370978
Comparison of 3 Rates for the Continuous Infusion of Mivacurium During Ambulatory Vitreoretinal Surgery Under General Anesthesia: A Prospective, Randomized, Controlled Clinical Trial
Abstract
Purpose: Mivacurium, the shortest-acting benzylisoquinoline nondepolarizing neuromuscular blocker used in clinical practice, is suitable for short-term ambulatory operations under general anesthesia. We investigated the neuromuscular blockade effect of different maintenance doses of mivacurium during ambulatory vitreoretinal surgery under general anesthesia and tried to determine the appropriate maintenance dose.
Patients and methods: Ninety-nine patients undergoing general anesthesia for elective ambulatory vitreoretinal surgery were randomly divided into three groups using the random number table method. Patients received three maintenance doses of mivacurium during surgery as follows: 3 μg/(kg·min) in group M1 (n = 33), 6 μg/(kg·min) in group M2 (n = 33), and 9 μg/(kg·min) in group M3 (n = 33). The primary outcome was the time from mivacurium withdrawal to a train-of-four stimulation ratio (TOFr) ≥ 0.9, and the secondary outcomes were the time from mivacurium withdrawal to TOFr ≥ 0.7, extubation time, incidence of TOFr < 0.9 after surgery and neuromuscular block effect.
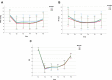
Results: The time from mivacurium withdrawal to TOFr ≥ 0.9 and to TOFr ≥ 0.7 was significantly longer in group M3 than in groups M1 and M2 (25.6±7.2 min vs 16.4±5.9 min and 18.6±5.3 min, P < 0.001; 22.1±6.3 min vs 13.6 ± 5.8 min and 15.5 ± 4.8 min; P < 0.001, respectively). There was a significant difference in the extubation time, the incidence of TOFr < 0.9 during extubation and upon leaving the operating room between group M3 and group M1 (all P < 0.05), but there was no such significant difference between group M2 and group M1 (all P > 0.05). The intraoperative depth of neuromuscular blockade in the three groups was significantly different, with 69.7% shallow block in group M1, 75.8% moderate block in group M2 and 63.6% deep block in group M3 (P < 0.001). One patient in group M1 experienced slight body movement during the operation.
Conclusion: An intraoperative continuous infusion of 6 μg/(kg·min) mivacurium can not only achieve good postoperative recovery but also provide a satisfactory neuromuscular blockade effect during surgery, and this maintenance dose is suitable for neuromuscular blockade during ambulatory vitreoretinal surgery.
Keywords: mivacurium; neuromuscular blocking agents; neuromuscular monitoring; postoperative period; vitreoretinal surgery.
© 2022 Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Recovery from mivacurium block with or without anticholinesterase following continuous infusion in obstetric patients.Anaesth Intensive Care. 1996 Oct;24(5):585-9. doi: 10.1177/0310057X9602400514. Anaesth Intensive Care. 1996. PMID: 8909671 Clinical Trial.
-
Time course and train-of-four fade of mivacurium block during sevoflurane and intravenous anaesthesia.Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2005 Apr;22(4):303-6. doi: 10.1017/s0265021505000517. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2005. PMID: 15892410 Clinical Trial.
-
[Continuous administration of mivacurium for short procedures. Delayed onset and recovery from neuromuscular blockade].Ann Fr Anesth Reanim. 1995;14(6):467-71. doi: 10.1016/s0750-7658(05)80486-1. Ann Fr Anesth Reanim. 1995. PMID: 8745969 Clinical Trial. French.
-
[The clinical pharmacology of new benzylisoquinoline-diester compounds, with special consideration of cisatracurium and mivacurium].Anaesthesist. 1997 Oct;46(10):840-9. doi: 10.1007/s001010050477. Anaesthesist. 1997. PMID: 9424966 Review. German.
-
Mivacurium. A review of its pharmacology and therapeutic potential in general anaesthesia.Drugs. 1993 Jun;45(6):1066-1089. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199345060-00009. Drugs. 1993. PMID: 7691494 Review.
Cited by
-
A comparison of the time course of action and laryngeal mask airway insertion conditions with different doses of mivacurium for day-case urologic surgery in children: a prospective cohort study.Front Pediatr. 2024 Feb 26;12:1330737. doi: 10.3389/fped.2024.1330737. eCollection 2024. Front Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 38468874 Free PMC article.
-
Optimal dose of mivacurium for laser-assisted laryngeal microsurgery: a pharmacokinetic study using closed-loop target-controlled infusion.Anaesthesiol Intensive Ther. 2024;56(4):231-240. doi: 10.5114/ait.2024.145249. Anaesthesiol Intensive Ther. 2024. PMID: 39917969 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Gropper MA, Miller RD, Eriksson LI, et al. Miller’s Anesthesia. Vol. 2. Set E-Book; 2019.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources