Guanmaitong Granule Attenuates Atherosclerosis by Inhibiting Inflammatory Immune Response in ApoE-/- Mice Fed High-Fat Diet
- PMID: 36148321
- PMCID: PMC9489104
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S372143
Guanmaitong Granule Attenuates Atherosclerosis by Inhibiting Inflammatory Immune Response in ApoE-/- Mice Fed High-Fat Diet
Abstract
Background: Atherosclerosis (AS) is the leading cause of cardiovascular diseases, such as myocardial infarction and stroke. Guanmaitong granule (GMTG) is a TCM (Traditional Chinese medicine) prescribed to treat AS. However, its mechanism remains unclear.
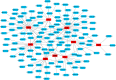
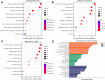
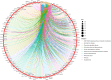
Methods: We obtained reliable ingredients and targets of GMTG using the HERB database. AS-related targets were obtained from HERB and GeneCards databases. The target database was constructed by intersecting the ingredients of GMTG with the AS-related targets. STRING and Cytoscape were used to create protein-protein interaction (PPI) network and screen core targets. GO enrichment analysis and KEGG pathway analyses were performed using R. Finally, the ApoE-/- mice AS model was induced by a high-fat diet (HFD) for in vivo validation of core pathways and targets.
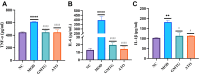
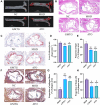
Results: A total of 124 ingredients and 418 potential targets of GMTG for treating AS were obtained. Numerous ingredients and targets were related to Panax notoginseng, Salvia miltiorrhiza, and Astragalus. Most core targets and pathways were involved in the inflammatory immune response. GMTG could decrease serum triglycerides, total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol, and oxidized low-density lipoprotein level and increase the serum high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol level. Furthermore, GMTG reduced the plaque burden and promoted plaque remodeling by reducing plaque area, lipid deposition, foam cell content, and collagen fiber content in the plaque in the aortic root of ApoE-/- mice. GMTG inhibited systemic and plaque inflammatory immune response and increased plaque stability by inhibiting the excessive release of the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway-induced inflammatory cytokines, tumor necrosis factor, interleukin-6, and interleukin-1 beta.
Conclusion: Radix notoginseng, Radix salviae liguliobae, and Radix astragali are the main ingredients of GMTG for treating AS. Further, GMTG could regulate the level of serum lipids and inhibit inflammatory immune response, which resulted in anti-AS effects such as plaque stabilization, reduction of plaque burden, and plaque remodeling. GMTG is a promising multi-target treatment for AS.
Keywords: Guanmaitong granule; atherosclerosis; inflammatory immune response; plaque burden; plaque remodeling.
© 2022 Yang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures







Similar articles
-
[Effects of Buyang Huanwu Decoction and Astragali Radix-Angelicae Sinensis Radix combination on inflammatory responses in atherosclerotic mice].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2023 Aug;48(15):4164-4172. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20230418.401. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 37802785 Chinese.
-
ZeXieYin formula alleviates atherosclerosis by inhibiting the MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway in APOE-/- mice to attenuate vascular inflammation and increase plaque stability.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Jun 12;327:117969. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.117969. Epub 2024 Mar 2. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38437888
-
Yang-Xin-Shu-Mai granule alleviates atherosclerosis by regulating macrophage polarization via the TLR9/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Jan 10;318(Pt A):116868. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116868. Epub 2023 Jul 16. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37454749
-
Apolipoproteins as potential communicators play an essential role in the pathogenesis and treatment of early atherosclerosis.Int J Biol Sci. 2023 Aug 21;19(14):4493-4510. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.86475. eCollection 2023. Int J Biol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37781031 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multidirectional Intervention of Chinese Herbal Medicine in the Prevention and Treatment of Atherosclerosis: From Endothelial Protection to Immunomodulation.Am J Chin Med. 2024;52(4):925-947. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X24500381. Epub 2024 May 27. Am J Chin Med. 2024. PMID: 38798151 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent advances of traditional Chinese medicine against cardiovascular disease: overview and potential mechanisms.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Sep 30;15:1366285. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1366285. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39403576 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

