Gene-environment interaction using polygenic scores: Do polygenic scores for psychopathology moderate predictions from environmental risk to behavior problems?
- PMID: 36148872
- PMCID: PMC7613991
- DOI: 10.1017/S0954579422000931
Gene-environment interaction using polygenic scores: Do polygenic scores for psychopathology moderate predictions from environmental risk to behavior problems?
Abstract
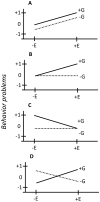
The DNA revolution has energized research on interactions between genes and environments (GxE) by creating indices of G (polygenic scores) that are powerful predictors of behavioral traits. Here, we test the extent to which polygenic scores for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and neuroticism moderate associations between parent reports of their children's environmental risk (E) at ages 3 and 4 and teacher ratings of behavior problems (hyperactivity/inattention, conduct problems, emotional symptoms, and peer relationship problems) at ages 7, 9 and 12. The sampling frame included up to 6687 twins from the Twins Early Development Study. Our analyses focused on relative effect sizes of G, E and GxE in predicting behavior problems. G, E and GxE predicted up to 2%, 2% and 0.4%, respectively, of the variance in externalizing behavior problems (hyperactivity/inattention and conduct problems) across ages 7, 9 and 12, with no clear developmental trends. G and E predictions of emotional symptoms and peer relationship problems were weaker. A quarter (12 of 48) of our tests of GxE were nominally significant (p = .05). Increasing the predictive power of G and E would enhance the search for GxE.
Keywords: behavior problems; genotype–environment interaction; polygenic scores; twins.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genetic Liability for Schizophrenia and Childhood Psychopathology in the General Population.Schizophr Bull. 2021 Jul 8;47(4):1179-1189. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbaa193. Schizophr Bull. 2021. PMID: 33561255 Free PMC article.
-
The p factor: genetic analyses support a general dimension of psychopathology in childhood and adolescence.J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2020 Jan;61(1):30-39. doi: 10.1111/jcpp.13113. Epub 2019 Sep 20. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 31541466 Free PMC article.
-
Polygenic Scores and Networks of Psychopathology Symptoms.JAMA Psychiatry. 2024 Sep 1;81(9):902-910. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2024.1403. JAMA Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38865107 Free PMC article.
-
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder polygenic risk scores predict attention problems in a population-based sample of children.J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2014 Oct;53(10):1123-9.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.jaac.2014.06.014. Epub 2014 Aug 19. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2014. PMID: 25245356
-
Gene-environment interplay in externalizing behavior from childhood through adulthood.J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2022 Oct;63(10):1206-1213. doi: 10.1111/jcpp.13652. Epub 2022 Jun 29. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35766296 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Gene-environment interaction in ADHD traits: the role of school environment, personality, callousness-unemotional traits and satisfaction with life.Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2025 Jul;34(7):2205-2214. doi: 10.1007/s00787-024-02628-y. Epub 2025 Jan 6. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 39760858 Free PMC article.
-
Gene-by-Environment Interaction Effects of Social Adversity on Externalizing Behavior in ABCD Youth.Behav Genet. 2023 May;53(3):219-231. doi: 10.1007/s10519-023-10136-z. Epub 2023 Feb 16. Behav Genet. 2023. PMID: 36795263 Free PMC article.
-
No gene by stressful life events interaction on individual differences in adults' self-control.Front Psychiatry. 2024 Apr 17;15:1388264. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1388264. eCollection 2024. Front Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38693999 Free PMC article.
-
Emotional and behavioral problems change the development of cerebellar gray matter volume, thickness, and surface area from childhood to adolescence: A longitudinal cohort study.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2023 Nov;29(11):3528-3548. doi: 10.1111/cns.14286. Epub 2023 Jun 8. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2023. PMID: 37287420 Free PMC article.
-
Research Review: A review of the past decade of family and genomic studies on adolescent mental health.J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2025 Jun;66(6):910-927. doi: 10.1111/jcpp.14099. Epub 2024 Dec 19. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 39697100 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arnau-Soler A, Macdonald-Dunlop E, Adams MJ, Clarke T-K, MacIntyre DJ, Milburn K, Navrady L, Hayward C, McIntosh AM, Thomson PA, Wray NR, et al. Genome-wide by environment interaction studies of depressive symptoms and psychosocial stress in UK Biobank and Generation Scotland. Translational Psychiatry. 2019;9:14. doi: 10.1038/s41398-018-0360-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

