Acupuncture for treating overactive bladder in adults
- PMID: 36148895
- PMCID: PMC9502659
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD013519.pub2
Acupuncture for treating overactive bladder in adults
Abstract
Background: Overactive bladder is a common, long-term symptom complex, which includes frequency of micturition, urgency with or without associated incontinence and nocturia. Around 11% of the population have symptoms, with this figure increasing with age. Symptoms can be linked to social anxiety and adaptive behavioural change. The cost of treating overactive bladder is considerable, with current treatments varying in effectiveness and being associated with side effects. Acupuncture has been suggested as an alternative treatment.
Objectives: To assess the effects of acupuncture for treating overactive bladder in adults, and to summarise the principal findings of relevant economic evaluations.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Incontinence Specialised Register, which contains trials identified from the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), MEDLINE (including In-Process, Epub Ahead of Print, Daily), ClinicalTrials.gov and WHO ICTRP (searched 14 May 2022). We also searched the Allied and Complementary Medicine database (AMED) and bibliographic databases where knowledge of the Chinese language was necessary: China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI); Chinese Science and Technology Periodical Database (VIP) and WANFANG (China Online Journals), as well as the reference lists of relevant articles. SELECTION CRITERIA: We included randomised controlled trials (RCTs), quasi-RCTs and cross-over RCTs assessing the effects of acupuncture for treating overactive bladder in adults.
Data collection and analysis: Four review authors formed pairs to assess study eligibility and extract data. Both pairs used Covidence software to perform screening and data extraction. We assessed risk of bias using Cochrane's risk of bias tool and assessed heterogeneity using the Chi2 testand I2 statistic generated within the meta-analyses. We used a fixed-effect model within the meta-analyses unless there was a moderate or high level of heterogeneity, where we employed a random-effects model. We used the GRADE approach to assess the certainty of evidence.
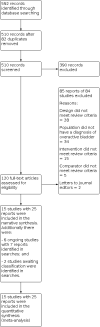
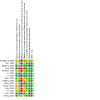
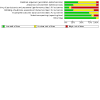
Main results: We included 15 studies involving 1395 participants in this review (14 RCTs and one quasi-RCT). All included studies raised some concerns regarding risk of bias. Blinding of participants to treatment group was only achieved in 20% of studies, we considered blinding of outcome assessors and allocation concealment to be low risk in only 25% of the studies, and random sequence generation to be either unclear or high risk in more than 50% of the studies. Acupuncture versus no treatment One study compared acupuncture to no treatment. The evidence is very uncertain regarding the effect of acupuncture compared to no treatment in curing or improving overactive bladder symptoms and on the number of minor adverse events (both very low-certainty evidence). The study report explicitly stated that no major adverse events occurred. The study did not report on the presence or absence of urinary urgency, episodes of urinary incontinence, daytime urinary frequency or episodes of nocturia. Acupuncture versus sham acupuncture Five studies compared acupuncture with sham acupuncture. The evidence is very uncertain about the effect of acupuncture on curing or improving overactive bladder symptoms compared to sham acupuncture (standardised mean difference (SMD) -0.36, 95% confidence interval (CI) -1.03 to 0.31; 3 studies; 151 participants; I2 = 65%; very low-certainty evidence). All five studies explicitly stated that there were no major adverse events observed during the study. Moderate-certainty evidence suggests that acupuncture probably makes no difference to the incidence of minor adverse events compared to sham acupuncture (risk ratio (RR) 1.28, 95% CI 0.30 to 5.36; 4 studies; 222 participants; I² = 0%). Only one small study reported data for the presence or absence of urgency and for episodes of nocturia. The evidence is of very low certainty for both of these outcomes and in both cases the lower confidence interval is implausible. Moderate-certainty evidence suggests there is probably little or no difference in episodes of urinary incontinence between acupuncture and sham acupuncture (mean difference (MD) 0.55, 95% CI -1.51 to 2.60; 2 studies; 121 participants; I2 = 57%). Two studies recorded data regarding daytime urinary frequency but we could not combine them in a meta-analysis due to differences in methodologies (very low-certainty evidence). Acupuncture versus medication Eleven studies compared acupuncture with medication. Low-certainty evidence suggests that acupuncture may slightly increase how many people's overactive bladder symptoms are cured or improved compared to medication (RR 1.25, 95% CI 1.10 to 1.43; 5 studies; 258 participants; I2 = 19%). Low-certainty evidence suggests that acupuncture may reduce the incidence of minor adverse events when compared to medication (RR 0.34, 95% CI 0.26 to 0.45; 8 studies; 1004 participants; I² = 51%). The evidence is uncertain regarding the effect of acupuncture on the presence or absence of urinary urgency (MD -0.40, 95% CI -0.56 to -0.24; 2 studies; 80 participants; I2 = 0%; very low-certainty evidence) and episodes of urinary incontinence (MD -0.33, 95% CI -2.75 to 2.09; 1 study; 20 participants; very low-certainty evidence) compared to medication. Low-certainty evidence suggests there may be little to no effect of acupuncture compared to medication in terms of daytime urinary frequency (MD 0.73, 95% CI -0.39 to 1.85; 4 studies; 360 participants; I2 = 28%). Acupuncture may slightly reduce the number of nocturia episodes compared to medication (MD -0.50, 95% CI -0.65 to -0.36; 2 studies; 80 participants; I2 = 0%, low-certainty evidence). There were no incidences of major adverse events in any of the included studies. However, major adverse events are rare in acupuncture trials and the numbers included in this review may be insufficient to detect these events.
Authors' conclusions: The evidence is very uncertain about the effect acupuncture has on cure or improvement of overactive bladder symptoms compared to no treatment. It is uncertain if there is any difference between acupuncture and sham acupuncture in cure or improvement of overactive bladder symptoms. This review provides low-certainty evidence that acupuncture may result in a slight increase in cure or improvement of overactive bladder symptoms when compared with medication and may reduce the incidence of minor adverse events. These conclusions must remain tentative until the completion of larger, higher-quality studies that use relevant, comparable outcomes. Timing and frequency of treatment, point selection, application and long-term follow-up are other areas relevant for research.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02047032 NCT02452879 NCT05158361 NCT03087578.
Copyright © 2022 The Cochrane Collaboration. Published by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
In accordance with Cochrane's
EH: is a practising NHS physiotherapist (Newcastle upon Tyne Hospital NHS Foundation Trust) and uses acupuncture as one of a number of relevant interventions within their practice. KB: none to declare. GB: none to declare. CH: is a subject matter specialist engaged with several parties including Medronic, Allergan, Astellas and Teleflex Medical, and is the guidelines panel chair for the European Association of Urology. YYZ: none to declare. NBK: none to declare. XZ: none to declare. CEC: provides acupuncture education courses, including a course on acupuncture for women's health that discusses overactive bladder treatment strategies.
Figures


















Update of
- doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013519
References
References to studies included in this review
Aydoğmuş 2014 {published data only}
-
- Aydoğmuş Y, Sunay M, Arslan H, Aydın A, Adiloğlu AK, Şahin H. Acupuncture versus solifenacin for treatment of overactive bladder and its correlation with urine nerve growth factor levels: a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Urologia Internationalis 2014;93(4):437-43. [DOI: 10.1159/000358202] [sr-incont64828] - DOI - PubMed
Chen 2009 {published data only}
-
- Chen Z, Han C, Wang G. 24 cases of overactive bladder treated by electroacupuncture [for information only English title translated via Google Translate™] [电针治疗膀胱过度活动症24例]. Journal of Clinical Acupuncture and Moxibustion 2009;25(8):22. [sr-incont99150]
Engberg 2009 {published data only}
Hong 2015 {published data only}
-
- Hong LJ, Zhao J, Zheng GH. Clinical study on electro-acupuncture for the treatment of mixed urinary incontinence [电针治疗混合性尿失禁的临床研究]. Journal of Clinical Acupuncture and Moxibustion 2015;31(11):1-4. [sr-incont70299]
Kelleher 1994 {published data only}
-
- Kelleher CJ, Filshie J, Burton G, Khullar V, Cardozo LD. Acupuncture and the treatment of irritative bladder symptoms. Acupuncture in Medicine 1994;12(1):9-12.
Lin 2020 {published data only}
-
- Lin Z, Chan YT. A randomized controlled trial to assess the effectiveness and safety of acupuncture for overactive bladder: a study in Hong Kong patient population [針刺治療膀胱過度活躍症的臨床試驗研究]. chictr.org.cn/hvshowproject.aspx?id=11255 (first received 19 February 2016). [ChiCTR-INR-16010048] [sr-incont77989]
-
- Lin ZX, Chan NH, Kwan YK, Chan YT, Zhang H, Tam KS, et al. A randomized controlled trial to assess the effectiveness and safety of acupuncture for overactive bladder: a study in Hong Kong population. Chinese Medicine 2020;15(1):108. [DOI: 10.1186/s13020-020-00388-w] [ChiCTR-INR-16010048] [sr-incont90242] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Liu 2019 {published data only}
-
- Kang J, Sun Y, Su T, Liu Y, Liang F, Liu Z. Electroacupuncture for balanced mixed urinary incontinence: secondary analysis of a randomized non-inferiority controlled trial. International Urogynecology Journal 2021;32(2):325-34. [NCT02047032] [sr-incont89529] - PubMed
-
- Liu B, Liu Y, Qin Z, Zhou K, Xu H, He L, et al. Electroacupuncture versus pelvic floor muscle training plus solifenacin for women with mixed urinary incontinence: a randomized noninferiority trial. Mayo Clinic Proceedings 2019;94(1):54-65. [DOI: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2018.07.021] [NCT02047032] [sr-incont78561] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Liu B, Wang Y, Xu H, Chen Y, Wu J, Mo Q, et al. Effect of electroacupuncture versus pelvic floor muscle training plus solifenacin for moderate and severe mixed urinary incontinence in women: a study protocol. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2014;14:301. [DOI: 10.1186/1472-6882-14-301] [NCT02047032] [sr-incont62533] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Liu Z, NCT02047032. Effect of electroacupuncture versus PFMT plus solifenacin for mixed urinary incontinence [Effect of electroacupuncture versus PFMT plus solifenacin for moderate and severe mixed urinary incontinence in female: a multicenter, noninferiority, randomized controlled trial]. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02047032 (first received 28 January 2014). [NCT02047032] [sr-incont60908]
Shen 2020 {published data only}
-
- Shen J, Luo YR, Meng YJ, Zhang YL, Qin PG, Ke LP, et al. Clinical study of electro-acupuncture in the treatment of female overactive bladder [for information only English title translated via Google Translate™] [电针疗法治疗女性膀胱过度活动症的临床研究]. Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine 2020;40(8):1000-4. [DOI: 10.7661/j.cjim.20200531.068] [sr-incont99172] - DOI
Solberg 2016 {published data only}
Wang 2011 {published data only}
-
- Lui J. Clinical Study on Treatment of Female Kidney-Qi Insufficiency Type Overactive Bladder by Electro-Acupuncture at Weizhong and Feiyang Point [Masters thesis]. Chengdu, Sichuan Province (China): Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019. [DOI: 10.26988/d.cnki.gcdzu.2019.000151] - DOI
-
- Wang XL, Shi YZ. Clinical study on acupuncture for overactive bladder (kidney-qi deficiency type) in elderly women [for information only English title translated via Google Translate™] [针刺治疗老年女性膀胱过度活动症(肾气亏虚型)的临床研究]. Guide of Chinese Medicine 2011;9(32):176-7. [ISSN: 1671-8194] [sr-incont99173]
Wang 2013a {published data only}
-
- Wang B, Xiao YP, Fan K, Huang CJ. Treatment of female overactive bladder with acupuncture [针灸治疗女性膀胱过度活动症的临床研究]. Journal of Beijing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine 2013;36(10):713-6. [ISSN: 1006-2157] [sr-incont99174]
Yang 2016 {published data only}
-
- Yang WY. 电针中髎, 会阳穴治疗膀胱过度活动症临床疗效观察 [Masters thesis] [Clinical Observation of Electroacupuncture at Zhongliao and Huiyang Points in the Treatment of Overactive Bladder. For information only English title translated via Google Translate™]. Beijing (China): Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, 2016. [sr-incont89283]
Yu 2012 {published data only}
-
- Yu, HZ. 电针治疗膀胱过度活动症的临床初探 [Masters thesis] [Clinical Preliminary Study on Electroacupuncture for Overactive Bladder. For information only English title translated via Google Translate™]. Beijing (China): Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, 2015. [sr-incont89282]
-
- Yu X, Wang J. 24 cases of overactive bladder treated by acupuncture [for information only English title translated via Google Translate™] [针刺治疗膀胱过度活动症24例]. Shandong Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine 2011;30(4):245-6. [DOI: 10.16295/j.cnki.0257-358x.2011.04.039] [sr-incont99177] - DOI
-
- Yu X, Wang J. Acupuncture therapy in treating 24 cases of overactive bladder. International Journal of Clinical Acupuncture 2012;21(3):113-4. [sr-incont72480]
Yuan 2015 {published data only}
-
- Yuan Z, He C. Acupuncture for overactive bladder in female adult: a randomized controlled trial (Abstract number 125). In: 45th Annual Meeting of the International Continence Society (ICS); 2015 Oct 6-9; Montreal, Canada. 2015. [ChiCTR-TRC-14005243] [sr-incont68771]
References to studies excluded from this review
Anhari 2011 {published data only}
-
- Anhari I. Comparative effects acupuncture and tolterodine on decreasing overactive bladder symptom score on overactive bladder. International Journal of Clinical Acupuncture 2011;20(2):49.
Cai 2017 {published data only}
-
- Cai S. Clinical study on acupuncture and nursing intervention in the treatment of female overactive bladder [针灸及护理干预治疗女性膀胱过度活动症的临床研究]. Chinese Community Doctors 2017;33(8):123, 125.
Carmona 2013 {published data only}
-
- Carmona MV, Molleja ÁM, Ríos IL, Torronteras AR, Tamajón VM, Obrero IG. Percutaneous tibial nerve stimulation versus neurostimulation of SP 6 (Sanyinjiao) in urge incontinence [Neuroestimulación percutánea del nervio tibial posterior frente a neuroestimulación de B 6 (Sanyinjiao) en incontinencia urinaria de urgencia]. Revista Internacional De Acupuntura 2013;7(4):124-30. [DOI: 10.1016/S1887-8369(13)70102-9] - DOI
Chen 2003 {published data only}
-
- Chen YL, Chen GM, Ge LB, Ha LF, Zong L. Effect of acupuncture different points on unstable bladder. Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science 2003;1(3):22-4.
Chen 2005a {published data only}
-
- Chen Yl, Cen J, Hou WG, Gao ZQ, Wang XY, Peng HD. Clinical study on different needling methods for unstable bladder of kidney deficiency [不同针刺方法对肾虚型不稳定膀胱排尿状况的临床研究]. Shanghai Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine 2005;39(7):43-4.
Chen 2005b {published data only}
-
- Chen YL, Ha LF, Cen J, Huang QR, Hou WG, Gao ZQ. Comparative observation on therapeutic effects of electroacupuncture and manual acupuncture on female urethral syndrome. Chinese Acupuncture and Moxibustion 2005;25(6):425-6. - PubMed
Chen 2012 {published data only}
-
- Chen YL, Feng WJ, Zhang XL. Parkinson’s disease combined with overactive bladder syndrome treated with acupuncture and medication [针药结合治疗帕金森病合并膀胱过度活动症]. Chinese Acupuncture and Moxibustion 2012;32(3):215-8. - PubMed
Chen 2015a {published data only}
-
- Chen YX, Ma RJ. Clinical observation of electroacupuncture at Huiyang (BL35) and Zhongliao (BL33) plus scalp acupuncture for female stress urinary incontinence [电针会阳、中髎穴结合头针治疗女性压力性尿失禁临床观察]. Shanghai Journal of Acupuncture and Moxibustion 2015;34(12):1159-61.
Chen 2015b {published data only}
-
- 陈楚红, 龚旻, 顾勇刚, 胡巍. Acupuncture combined with doxazosin mesylate controlled-release tablets in the treatment of chronic prostatitis complicated with overactive bladder [for information only English title translated via Google Translate™] [针刺联合甲磺酸多沙唑嗪控释片治疗慢性前列腺炎合并膀胱过度活动症]. In: 第十次全国中西医结合男科学术大会、第六次广西中医、中西医结合男科学术大会、全国中西医结合男科疾病诊疗新进展学习班. 2015.
Chen 2015c {published data only}
-
- Chen X, Chen J, Tang SL. Efficacy observation of electroacupuncture combined with tolterodine in the treatment of 48 cases of female overactive bladder [for information only English title translated via Google Translate™] [电针联合托特罗定治疗女性膀胱过度活动症48例疗效观察]. Hainan Medical Journal 2015;26(1):127-8.
Cheung 2018 {published data only}
-
- Cheung YK, Law PM, Lee LL, Ng K, Chan SC. Acupuncture for urinary incontinence in Chinese women: a randomized controlled trial (Abstract 30). Neurourology and Urodynamics 2018;37(Suppl 5):S78-9.
Dunning 2017 {published data only}
-
- Dunning J, NCT03238716. Neuromuscular re-eduaction, [sic] exercise and electric dry needling vs. neuromuscular re-education and exercise for stress urinary incontinence [Neuromuscular re-education, impairment-based exercise and electric dry needling vs. neuromuscular re-education and impairment-based exercise for stress urinary incontinence]. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT03238716 (first received 3 August 2017).
Ellis 1990 {published data only}
-
- Ellis N, Briggs R, Dowson D. The effect of acupuncture on nocturnal urinary frequency and incontinence in the elderly. Complementary Medicine Research 1990;4(1):16-8.
Emmons 2005 {published data only}
-
- Emmons SL, Otto L. Acupuncture for overactive bladder: a randomized controlled trial. Obstetrics and Gynecology 2005;106(1):138-43. - PubMed
Enberg 2006 {published data only}
-
- Engberg S, NCT00297427. Acupuncture for urinary incontinence [Efficacy of acupuncture in treating urinary incontinence]. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00297427 (first received 28 February 2006). [NCT00177450 (obsolete)]
Feng 2011 {published data only}
-
- Feng W, Chen Y, Zhang X. Research on acupuncture combined with small dose of tolterodine in the treatment of overactive bladder symdrom in Parkinson's disease [针刺联合小剂量托特罗定治疗帕金森病合并膀胱过度活动症]. Chinese Journal of Practical Nervous Diseases 2011;14(16):7-10. [ISSN: 1673-5110]
Feng 2014 {published data only}
-
- Feng QT, He B, Chen XL, Li RH. Clinical observation of different acupuncture methods for treating overactive bladder syndrome. Journal of New Chinese Medicine 2014;46(12):188-90. [CENTRAL: CN-01427256]
Guo 2016 {published data only}
-
- Guo Y, Yang X, Wang Y, Wang X, Jiang Y, Xiong W. A comparative study on the application of pure acupuncture and solifenacin succinate in the treatment of women with overactive bladder [for information only English title translated via Google Translate™] [应用单纯针灸疗法与琥珀酸索利那新治疗女性膀胱过度活动症的对比性研究]. Journal of Emergency in Traditional Chinese Medicine 2016;25(11):2193-5. [DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-745X.2016.11.062] - DOI
He 2016 {published data only}
-
- He E, Chen Y, Tian H, Zhao J. Effective observation of electroacupuncture with different courses for female stress urinary incontinence. Chinese Acupuncture and Moxibustion 2016;36(4):351-4. - PubMed
He 2018 {published data only}
-
- He T, Mo Q, ChiCTR1800018176. A randomized controlled trial for comparing electroacupuncture and warm acupuncture in the treatment of overactive bladder. chictr.org.cn/showproj.aspx?proj=30705 (first received 3 September 2018).
Hong 1996 {published data only}
-
- Hong Z. Combination of scalp acupuncture with body acupuncture for treating senile urinary incontinence. Journal of Chinese Medicine 1996;52:10-1.
Hu 2005 {published data only}
-
- Hu J. Acupuncture treatment of frequent urination. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine 2005;25(3):238-40. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Hu 2015 {published data only}
-
- Hu B, Zheng DB, Jing ZT, Wang JF. 30 cases of female urgent urinary incontinence treated by acupoint application of traditional Chinese medicine [for information only English title translated via Google Translate™] [中药穴位贴敷治疗女性急迫性尿失禁30 例]. 西部中医药 2015;28(12):109-10.
Hu 2016 {published data only}
-
- 胡碧川. A randomized controlled clinical study of oral tolterodine tablets combined with electroacupuncture on the four sacral points in the treatment of overactive bladder [for information only English title translated via Google Translate™] [口服托特罗定片联合电针骶四穴疗法治疗膀胱过度活动症的随机对照临床研究]. In: 中国中西医结合学会泌尿外科专业委员会第十四次全国学术会议暨2016年广东省中西医结合学会泌尿外科专业委员会学术年会. 2016.
Jiao 2019 {published data only}
-
- Jiao R, Liu Y, Liu B, Liu Z. Risk factors related to acupuncture response in postmenopausal women with stress urinary incontinence: secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial. Medicine 2019;98(16):e15220. [CLINICAL TRIAL: NCT01784172] [DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000015220] [PMID: ] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Johnstone 2003 {published data only}
Kim 2008 {published data only}
Kubista 1976 {published data only}
Kwon 2014 {published data only}
-
- Kwon JN, NCT02271607. The effect and safety of moxibustion therapy for overactive bladder patients [A pilot study about the effects of indirect-moxibustion on bladder- functional improvement and symptoms management in patients with overactive bladder: a randomized controlled trial]. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02271607 (first received 22 October 2014).
Lee 2016 {published data only}
-
- Lee LL, Chan SS, ChiCTRINR16007766. Acupuncture for urinary incontinence in Chinese women: a randomized controlled trial [針灸用於處理華人婦女小便失禁問題之隨機研究]. chictr.org.cn/showproj.aspx?proj=13144 (first received 11 January 2016).
Liao 2007 {published data only}
-
- Liao X, Tang H, Xiao P. 35 cases of overactive bladder treated by electroacupuncture at Zhongliao point [for information only English title translated via Google Translate™] [电针中髎穴为主治疗膀胱过度活动症35例]. Journal of Clinical Acupuncture and Moxibustion 2007;23(1):35-6.
Liao X 2007 {published data only}
-
- 廖小七, 唐华, 肖鹏. 35 cases of overactive bladder treated by electroacupuncture at Zhongliao point [for information only English title translated via Google Translate™] [电针中髎穴为主治疗膀胱过度活动症35例]. Journal of Clinical Acupuncture and Moxibustion 2007;23(1):35-6.
Lillie 2014 {published data only}
-
- Lillie R. News from the front: Professor Si-you Wang: pudendal nerve stimulation for incontinence. Journal of the Acupuncture Association of Chartered Physiotherapists 2014;Autumn(1):129-30. [ISSN: 1748-8656]
Liu 1998 {published data only}
-
- Liu ZS, Shao SJ, Ye YM, Li YS, Huang M, Zhang H, et al. Analysis of the curative effect of electro-acupuncture at Ciliao & Huiyang points to treat senile urinary incontinence [电针次 、会阳治疗老年尿失禁疗效分析]. Shanghai Journal of Acupuncture and Moxibustion 1998;17(3):14-5.
Liu 2010 {published data only}
-
- 刘超. 中西医结合治疗膀胱过度活动症的临床观察 [Masters thesis] [Clinical Observation on Treatment of Overactive Bladder with Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine. For information only English title translated via Google Translate™]. Hubei (China): 湖北中医药大学, 2010.
Liu 2013 {published data only}
-
- Liu B, NCT01784172. Efficacy and safety study of electroacupuncture for simple female stress urinary incontinence-a multicenter trial [The efficacy and safety study of electro-acupuncture for simple female stress urinary incontinence - a multicenter, randomized controlled trial]. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01784172 (first received 5 February 2013).
Liu 2015a {published data only}
-
- Liu ZS, Xu HF, NCT02445573. Efficacy of electroacupuncture (EA) for women with pure stress urinary incontinence (SUI) [A pilot randomized placebo controlled trial of electroacupuncture for women with pure stress urinary incontinence]. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02445573 (first received 15 May 2015).
Liu 2015b {published data only}
-
- Liu Z, Chen H, Wu W, Luo Q, Huang X, Shen T, et al. The clinical observation in treating overactive bladder by the combination of tolterodine and electroacupuncture [托特罗定联合电针治疗膀胱过度活动症临床观察]. China Medical Innovation 2015;12(1):52-4. [DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-4985.2015.01.018] - DOI
Liu 2016 {published data only}
-
- Liu YM, Jin HY, Li ZQ. Effect of pelvic floor biofeedback combined with Huiyang acupuncture and moxibustion on muscle potential and quality of life in patients with postpartum urinary incontinence [盆底生物反馈结合针灸会阳穴对产后尿失禁患者肌电位及生活质量的影响]. Maternal and Child Health Care of China 2016;31(14):2799-801.
Liu 2017 {published data only}
Lu 2002 {published data only}
-
- Lu ZQ. Clinical analysis on scalp-plus body-acupuncture for treatment of senile urinary incontinence. World Journal of Acupuncture-Moxibustion 2002;12(2):50-2. [ISSN: 1003-5257]
Mao 2012 {published data only}
-
- Hou C, Gao W, Hu S. Clinical observation of M receptor antagonist combined with acupuncture in the treatment of overactive bladder [for information only English title translated via Google Translate™] [M受体拮抗剂与针刺疗法联合治疗膀胱过度活动症的临床观察]. Hubei Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine 2014;36(3):40-1.
-
- Mao HH. 针刺联合M受体拮抗剂优化治疗膀胱过度活动症的临床研究 [Masters thesis] [Acupuncture Combined M Receptor Antagonist Optimization Overactive BIadder CIinicaI Research]. Wuhan, Hubei (China): Hubei University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2012.
Miao 2015 {published data only}
-
- Miao G, Jia M, Zhang X. Efficacy observation of electroacupuncture combined with pelvic floor muscle training in the treatment of female overactive bladder [for information only English title translated via Google Translate™] [电针联合盆底肌训练治疗女性膀胱过度活动症的疗效观察]. Journal of Emergency in Traditional Chinese Medicine 2015;24(11):2054-6.
Nam 2017 {published data only}
-
- Nam EY, Kim DI, NCT03260907. Efficacy and safety of electroacupuncture and acupuncture in postmenopausal women with overactive bladder [Efficacy and safety of electroacupuncture and acupuncture in postmenopausal women with overactive bladder; a multicenter, randomized, controlled, parallel clinical trial]. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT03260907 (first received 24 August 2017).
Pang 2018 {published data only}
-
- Pang R, NCT03450902. Chinese herbal therapy combined with acupuncture for female mixed urinary incontinence [Combination therapy with Chinese herbal formula, Yiqi Suoquan granule, and acupuncture for female mixed urinary incontinence]. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT03450902 (first received 1 March 2018).
Penson 2018 {published data only}
Philp 1988 {published data only}
Qu 2013 {published data only}
-
- Qu Y, Chen X, Qu M, Zhao R, Yu J, Wang S. 32 cases of overactive bladder treated by electroacupuncture [for information only English title translated via Google Translate™] [电针治疗膀胱过度活动症 32 例]. 中国保健营养: 下半月 2013;3:641.
Ren 2020 {published data only}
-
- Ren TT. Comparison of effects of acupuncture and solifenacin succinate tablets in treatment of female overactive bladder patients [for information only English title translated via Google Translate™] [针灸和琥珀酸索利那新片治疗女性膀胱过度活动症患者的效果比较]. Medical Journal of Chinese People’s Health 2020;32(6):115-7.
Rong 2015 {published data only}
-
- Rong Q. The quality of life effects acupuncture treatment for the female pelvic floor dysfunction [针灸治疗压力性尿失禁60例临床观察]. Chinese Journal of Ethnomedicine and Ethnopharmacy 2015;24(21):92-3; 95.
Ruan 2018 {published data only}
-
- Ruan L, ChiCTR1800014351. Clinical study of pelvic floor electrical stimulation combined with traditional Chinese medicine and acupoint sticking in the treatment of postpartum urinary incontinence [Clinical study of pelvic floor electrical stimulation combined with traditional Chinese medicine and acupoint sticking in the treatment of postpartum urinary incontinence (Qi Deficiency syndrome)]. trialsearch.who.int/Trial2.aspx?TrialID=ChiCTR1800014351 (first received 7 January 2018).
Shen 2012a {published data only}
-
- Shen YZ, Lin X, Lin Q. Overactive bladder after transurethral resection of prostate treated with electroacupuncture therapy and tolterodine [电针联合托特罗定治疗经尿道前列腺电切术后膀胱过度活动症]. Chinese Acupuncture and Moxibustion 2012;32(5):404-8. - PubMed
Shen 2012b {published data only}
-
- Shen YZ, Shen L. Electroacupuncture for overactive bladder after transurethral resection of prostate [电针治疗经尿道前列腺电切术后膀胱过度活动症效果]. Medical Journal of Qilu 2012;27(4):341-2, 5.
Su 2013 {published data only}
-
- Su TS, NCT01940432. The efficacy of electroacupuncture for treatment of simple female stress urinary incontinence: comparison with pelvic floor muscle training-a multicenter randomized controlled trial. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01940432 (first received 12 September 2013).
Su 2020a {published data only}
-
- Su YY, Zhao D, Lin MQ. Clinical observation of urine three-needling combined with tolterodine in treating overactive bladder [尿三针联合托特罗定治疗膀胱过度活动症的临床疗效观察]. Journal of Guangzhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine 2020;37(8):1495-500.
Su 2020b {published data only}
-
- Su Y, Zhao D, Lin MQ. Clinical observation of urine three-needling combined with tolterodine in the treatment of overactive bladder [尿三针联合托特罗定治疗膀胱过度活动症的临床疗效观察]. Journal of Guangzhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine 2020;37(8):1495-500.
Suen 2015 {published data only}
-
- Suen LK, NCT02330107. Auriculotherapy on lower urinary tract symptoms in elderly men [Effectiveness of auriculotherapy on lower urinary tract symptoms in elderly men: a randomized controlled feasibility study]. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02330107 (first received 1 January 2015).
Tang 2016 {published data only}
-
- Tang KM, Shen R, Jiang F, Wang Q, Xie XB, Chen YL. Therapeutic evaluation of acupuncture for female stress urinary incontinence [针刺治疗女性单纯性压力性尿失禁临床疗效评价]. Shanghai Journal of Acupuncture and Moxibustion 2016;35(12):1439-41.
Wan 2019 {published data only}
-
- Wan OY, Cheung YK, Law MP, Lee LL, Chan SS. A randomized controlled trial on the effect of acupuncture on urinary incontinence and quality of life in women (Abstract 96). Female Pelvic Medicine and Reconstructive Surgery 2019;25(5 Suppl):S74-5. [DOI: 10.1097/SPV.0000000000000763] - DOI
Wang 2008 {published data only}
-
- Wang HX, Cui H. Observation on the effect of electroacupuncture on senile urge urinary incontinence [for information only English title translated via Google Translate™] [电针治疗老年急迫性尿失禁疗效观察]. Chinese Journal of Information on Traditional Chinese Medicine 2008;15(2):70.
Wang 2013b {published data only}
-
- Wang YF, Pan ZL, Chen JJ, Zhang W, Meng L. Clinical study of electroacupuncture in the treatment of overactive bladder [for information only English title translated via Google Translate™] [电针疗法治疗膀胱过度活动症的临床研究]. Practical Clinical Journal of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine 2013;13(3):1-3.
Wang 2015 {published data only}
-
- Wang S, NCT02599831. Efficacy of electrical pudendal nerve stimulation for patients with post prostatectomy urinary incontinence. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02599831 (first received 9 November 2015).
Wang 2016 {published data only}
Wang 2017a {published data only}
Wang 2017b {published data only}
-
- Wang S, NCT02311634. A comparison of electrical pudendal nerve stimulation and transvaginal electrical stimulation for urge incontinence [A comparison of efficacies of electrical pudendal nerve stimulation versus transvaginal electrical stimulation in treating urge incontinence]. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02311634 (first received 8 December 2014).
Wang 2019 {published data only}
Xie 2020 {published data only}
-
- Xie N, Yang Y, Jiang HY. Clinical observation of applying acupuncture and nursing intervention in the treatment of overactive bladder [针灸及护理干预治疗膀胱过度活动症临床观察]. Journal of Sichuan of Traditional Chinese Medicine 2020;38(7):202-5.
Xiong 2020 {published data only}
-
- Xiong C, Tang Y, Shi R, Zhou YH, Sun S, Xiang Y, et al. Therapeutic effect of myofascial trigger point electroacupuncture technology on the treatment of overactive bladder syndrome in female [电针刺激肌筋膜触发点治疗女性膀胱过度活动症的临床疗效]. Journal of Central South University (Medical Science) 2020;45(2):155-9. - PubMed
Xu 2010 {published data only}
-
- 徐海蓉. 针刺治疗膀胱过度活动症的系统评价及中风后急迫性尿失禁电针疗效的 RCT 研究 [PhD thesis] [A Systematic Review of Acupuncture for Overactive Bladder and an RCT Study on the Efficacy of Electroacupuncture for Post-Stroke Urge Urinary Incontinence. For information only English title translated via Google Translate™]. 北京: 中国中医科学院, 2010.
Xu 2016 {published data only}
Yang 2020 {published data only}
-
- Xie N, Yue J, Jiang HY. Clinical observation of applying acupuncture and nursing intervention in the treatment of overactive bladder [针灸及护理干预治疗膀胱过度活动症临床观察]. Journal of Sichuan of Traditional Chinese Medicine 2020;38(7):202-5.
Zhang 1999 {published data only}
-
- Zhang H. Scalp acupuncture plus body acupuncture for senile urinary incontinence. International Journal of Clinical Acupuncture 1999;10:101-4.
Zhang 2012 {published data only}
-
- Zhang GT, Bao ZH, Zhang LD. Efficacy of solifenacin combined with electrical stimulation in the treatment of women with overactive bladder [for information only English title translated via Google Translate™] [索利那新联合电刺激治疗女性膀胱过度活动症的疗效]. Journal of Practical Medicine 2012;28(23):3990-2. [ISSN: 1006-5725]
Zhao 2012 {published data only}
-
- Zhao L. Acusector Overactive Bladder in 68 Cases of Disease Clinical Observation [电针参与治疗膀胱过度活动症68例临床观察] [Masters thesis]. Zhengzhou (China): Henan College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2012.
Zhao 2013 {published data only}
-
- Zhao L, Wang SY. Treatment frequency and long-term efficacy observation on electric pudendal nerve stimulation for stress urinary incontinence. Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science 2013;11(3):177-80. [DOI: 10.1007/s11726-013-0684-3] - DOI
Zhao 2013a {published data only}
-
- Zhao L, Wang SY. Efficacy impacts of the different treatment frequencies on female stress urinary incontinence. Chinese Acupuncture and Moxibustion 2013;33(12):1088-90. - PubMed
Zhao 2016 {published data only}
-
- Zhao J, Cui X, Lu Y, He X, Wen C. Clinical study of acupuncture combined with aconite cake-separated moxibustion in treating senile female stress urinary incontinence [针刺联合隔附子饼灸治疗老年女性压力性尿失禁临床研究]. World Chinese Medicine 2016;11(5):891-3.
Zheng 1990 {published data only}
-
- Zheng H, Sun Y, Xu Z, Hao M, Cao X. Urodynamic study of acupuncture and moxibustion on female stress urinary incontinence [for information only English title translated via Google Translate™] [针灸对女性压力性尿失禁的尿流动力学研究]. Shanghai Journal of Acupuncture and Moxibustion 1990;9(3):1-3.
Zheng 1992 {published data only}
-
- Zheng H, Sun Y, Xu Z, Hou M. Flow dynamics of urine in female patients with stress urinary incontinence treated by acupuncture and moxibustion. International Journal of Clinical Acupuncture 1992;3(3):243-7.
Zheng 2015 {published data only}
-
- Zheng HM, Xu SF, Yin P, Tang KM, Chen YL. Observation on short-term and long-term therapeutic effects of electro-acupuncture on mild and moderate stress urinary incontinence [电针治疗轻中度女性压力性尿失禁的近远期疗效观察]. World Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine 2015;10(2):191-3, 209.
Zhishun 2002 {published data only}
-
- Zhishun L, Baoyan L, Tao Y, Yongming Y, Hong Z, Wei Z, et al. Clinical study of electroacupuncture treatment of senile urge urinary incontinence. International Journal of Clinical Acupuncture 2002;13(4):255-62.
Zhong 2016 {published data only}
-
- Zhong P, Yu H, Zhou Q, Lu Z, Yang C. Clinical study of electroacupuncture combined with M receptor antagonist in optimal treatment of overactive bladder [for information only English title translated via Google Translate™] [电针联合M 受体拮抗剂优化治疗膀胱过度活动症的临床研究]. In: 中国中西医结合学会泌尿外科专业委员会第十四次全国学术会议暨 2016 年广东省中西医结合学会泌尿外科专业委员会学术年会论文集 2016 [The 14th National Academic Conference of the Urology Professional Committee of the Chinese Society of Chinese and Western Medicine and the 2016 Academic Conference of the Professional Committee of Urology of the Chinese and Western Medical Association of Guangdong Province. For information only English title translated via Google Translate™]. Vol. 1. 2016:1604-7.
Zhu 2018 {published data only}
-
- 朱彬彬, 童钟, 周世超, 成慧慧, 赵嫦莹, 萧韵雅. Observation of curative effect of acupuncture at Bliao point combined with injection of botulinum toxin type A in the treatment of overactive bladder after spinal cord injury [for information only English title translated via Google Translate™] [针刺八髎穴联合A型肉毒毒素注射治疗脊髓损伤后膀胱过度活动症疗效观察]. 河北中医 2018;40(5):759-62.
Zhu 2021 {published data only}
-
- Zhu Z, Bi Q. Analysis of the value of acupuncture in the treatment of frequent urination [for information only English title translated via Google Translate™] [针刺治疗尿频的价值分析]. Clinical Research 2021;29(2):113-4.
References to studies awaiting assessment
Bulut 2014 {published data only}
-
- Bulut BB, Kilic MA, Resim S, Efe E, Bahar MR, Koluş E. S231: Comparison between acupuncture treatment and tolteradine in overactive bladder. European Urology Supplements 2014;13(7):e1556. [DOI: 10.1016/S1569-9056(14)61758-9] [sr-incont99190] - DOI
Han 2011 {published data only}
-
- Han C. Clinical observation of electroacupuncture on 48 cases of overactive bladder [for information only English title translated via Google Translate™] [电针治疗膀胱过度活动症48例临床疗效观察]. In: 首届全国脑外伤治疗与康复学术大会论文汇编 (下) [First National Academic Conference on Treatment and Rehabilitation of Brain Trauma (Part 2) For information only English title translated via Google Translate™]. 2011. [sr-incont99545]
References to ongoing studies
Huang 2020 {published data only}
-
- Huang Y, Mo Q, ChiCTR1900027846. Randomized controlled trial for the efficacy of electroacupuncture in the treatment of acute urinary incontinence. chictr.org.cn/showprojen.aspx?proj=45632 (first received 30 November 2019). [ChiCTR1900027846] [sr-incont85138] [PARTNER REGISTRY: ChiMCTR1900025384]
-
- Huang Y, Qi S, Wu X, Zhi N, He T, Shen M, et al. Randomized controlled trial for the efficacy of electroacupuncture in the treatment of urge urinary incontinence: a clinical study protocol. Medicine 2020;99(9):e19315. [DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000019315] [ChiCTR1900027846] [sr-incont85335] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Jia 2015 {published data only}
-
- Jia BH, NCT02452879. Treatment, parallel assignment, double blind (subject, outcomes assessor), efficacy study [The effectiveness, superiority and safety of EA on OAB: multi-center randomized controlled trial]. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02452879 (first received 25 May 2015). [NCT02452879] [sr-incont68790]
Pang 2021 {published data only}
-
- Pang R, NCT05158361. Acupuncture for overactive bladder in adults [Effectiveness and safety of acupuncture for overactive bladder in adults: a random control clinical trial]. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT05158361 (first received 15 December 2021). [NCT05158361] [sr-incont98453]
Shen 2019 {published data only}
-
- Shen J, ChiCTR1900021372. A randomized controlled trial for the efficacy and safety of electro-acupuncture in the treatment of female overactive bladder [电针治疗女性膀胱过度活动症的有效性和安全性的随机对照试验]. chictr.org.cn/showproj.aspx?proj=36078 (first received 14 January 2019). [ChiCTR1900021372] [sr-incont78551]
Sheyn 2017 {published data only}
-
- Sheyn D, NCT03087578. Comparison of electroacupuncture to mirabegron for treatment of overactive bladder [Comparison of electroacupuncture to mirabegron on symptoms of overactive bladder in women who have failed anti-cholinergic therapy]. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT03087578 (first received 22 March 2017). [NCT03087578] [sr-incont76095]
Wen 2020 {published data only}
-
- Ning L, Qian W, ChiCTR1800019928. Clinical study for relieving symptoms of moderate and severe overactive bladder by electroacupuncture [Efficacy evaluation for electroacupuncture in the treatment of neurogenic urinary retention and overactive bladder]. chictr.org.cn/showproj.aspx?proj=33670 (first received 9 December 2018). [ChiCTR1800019928] [sr-incont78573]
Additional references
Abrams 2012
-
- Abrams P, Chapple CR, Jünemann KP, Sharpe S. Urinary urgency: a review of its assessment as the key symptom of the overactive bladder syndrome. World Journal of Urology 2012;30(3):385-92. - PubMed
Abrams 2017
-
- Abrams P, Cardozo L, Wagg A, Wein A. Incontinence: 6th International Consultation on Incontinence. Bristol (UK): ICI-ICS. International Continence Society, 2017. [ISBN: 978-09569607-3-3]
Al‐Janabi 2013
Aluko 2022
-
- Aluko P, Graybill E, Craig D, Henderson C, Drummond M, Wilson EC, et al, on behalf of the Campbell and Cochrane Economics Methods Group. Chapter 20: Economic evidence. In: Higgins JP, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, et al, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 6.3 (updated February 2022). Cochrane, 2022. Available from training.cochrane.org/handbook.
Avery 2004
Clarkson 2015
Covidence [Computer program]
-
- Covidence. Version accessed 2 January 2020. Melbourne, Australia: Veritas Health Innovation. Available at covidence.org.
CRD 2015
-
- Centre for Reviews and Dissemination (CRD). CRD database: search strategies. 2015. crd.york.ac.uk/crdweb/ (accessed 14 June 2019).
Deng 2015
Dhond 2008
Duthie 2011
EndNote 2018 [Computer program]
-
- EndNote. Version X8.2. Philadelphia (PA): Clarivate Analytics, 2018.
Forde 2016
Ganz 2010
GRADEpro GDT [Computer program]
-
- GRADEpro GDT. Version accessed 2 January 2020. Hamilton (ON): McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime). Available at gradepro.org.
Gray 2015
Herbison 2009
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Higgins 2019
-
- Higgins JP, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page M, et al editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.0 (updated August 2019). Cochrane, 2019. Available from training.cochrane.org/handbook.
Hiller 2002
-
- Hiller L, Radley S, Mann CH, Radley SC, Begum G, Pretlove SJ, et al. Development and validation of a questionnaire for the assessment of bowel and lower urinary tract symptoms in women. BJOG 2002;109(4):413-23. - PubMed
Hino 2010
-
- Hino K, Honjo H, Nakao M, Kitakoji H. The effects of sacral acupuncture on acetic acid-induced bladder irritation in conscious rats. Urology 2010;75(3):730-4. - PubMed
Hu 2003
-
- Hu TW, Wagner TH, Bentkover JD, LeBlanc K, Piancentini A, Stewart WF, et al. Estimated economic costs of overactive bladder in the United States. Urology 2003;61(6):1123-8. - PubMed
Huang 2012
Irwin 2006
-
- Irwin DE, Milsom I, Hunskaar S, Reilly K, Kopp Z, Herschorn S, et al. Population-based survey of urinary incontinence, overactive bladder, and other lower urinary tract symptoms in five countries: results of the EPIC study. European Urology 2006;50(6):1306-14; discussion 1314-5. - PubMed
Jimenez‐Cidre 2015
-
- Jimenez-Cidre MA, Lopez-Fando L, Esteban-Fuertes M, Prieto-Chaparro L, Llorens-Martinez FJ, Salinas-Casado J, et al. The 3-day bladder diary is a feasible, reliable and valid tool to evaluate the lower urinary tract symptoms in women. Neurourology and Urodynamics 2015;34(2):128-32. - PubMed
Lai 2016
Lim 2019
-
- Lim R, Liong ML, Lim KK, Leong WS, Yuen KH. The minimum clinically important difference of the International Consultation on Incontinence Questionnaires (ICIQ-UI SF and ICIQ-LUTSqol). Urology 2019;133:91-5. - PubMed
Maciocia 2007
-
- Maciocia G. The practice of Chinese medicine: the treatment of diseases with acupuncture and Chinese herbs. 2nd edition. London (UK): Churchill Livingstone, 2007. [ISBN: 9780443074905]
MacPherson 2001
MacPherson 2010
-
- MacPherson H, Altman DG, Hammerschlag R, Youping L, Taixiang W, White A, et al, on behalf of the STRICTA Revision Group. Revised STandards for Reporting Interventions in Clinical Trials of Acupuncture (STRICTA): extending the CONSORT statement. PLOS One 2010;7(6):e1000261. [DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000261] [PMC2882429] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Madhuvrata 2012
Malde 2018
-
- Malde S, Fry C, Schurch B, Marcelissen T, Averbeck M, Digesu A, et al. What is the exact working mechanism of botulinum toxin A and sacral nerve stimulation in the treatment of overactive bladder/detrusor overactivity? ICI-RS 2017. Neurourology and Urodynamics 2018;37(S4):S108-16. - PubMed
Napadow 2013
NICE 2019
-
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). Urinary incontinence and pelvic organ prolapse in women: management. NICE guideline [NG123]. Published: 2 April 2019; last updated: 24 June 2019. Available at nice.org.uk/guidance/ng123 (accessed 6 November 2019).
Ou 2019
Powell 2018
Pullman 2016
-
- Pullman M. Acupuncture for urogenital conditions. In: Filshie J, White A, Cummings M, editors(s). Medical Acupuncture: a Western Scientific Approach. 2nd edition. London (UK): Elsevier Health Sciences, 2016:475-86. [ISBN: 0702068551, 9780702068553]
Rabin 2001
-
- Rabin R, Charro F. EQ-5D: a measure of health status from the EuroQol Group. Annals of Medicine 2001;33(5):337-43. - PubMed
Rantell 2017
-
- Rantell A, Cardozo L, Khullar V. Personal goals and expectations of OAB patients in the UK. Neurourology and Urodynamics 2017;36(4):1194-200. - PubMed
RevMan Web 2020 [Computer program]
-
- Review Manager Web (RevManWeb). Version 2.3.0. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2020. Available at revman.cochrane.org.
Schünemann 2019
-
- Schünemann HJ, Higgins JP, Vist GE, Glasziou P, Akl EA, Skoetz N, et al. Chapter 14: Completing ‘Summary of findings’ tables and grading the certainty of the evidence. In: Higgins JP, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, et al (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.0 (updated July 2019). Cochrane, 2019. Available from training.cochrane.org/handbook.
Sexton 2011
-
- Sexton CC, Coyne KS, Thompson C, Bavendam T, Chen CI, Markland A. Prevalence and effect on health-related quality of life of overactive bladder in older Americans: results from the epidemiology of lower urinary tract symptoms study. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2011;59(8):1465-70. - PubMed
Stata 2019 [Computer program]
-
- Stata. Version 16. College Station, TX, USA: StataCorp LLC, 2019. Available at www.stata.com.
Tse 2016
-
- Tse V, King J, Dowling C, English S, Gray K, Millard R, et al. Conjoint Urological Society of Australia and New Zealand (USANZ) and Urogynaecological Society of Australasia (UGSA) Guidelines on the management of adult non-neurogenic overactive bladder. BJU International 2016;117(1):34-47. - PubMed
Tubaro 2004
-
- Tubaro A. Defining overactive bladder: epidemiology and burden of disease. Urology 2004;64(6 Suppl 1):2-6. - PubMed
Wallace 2004
Wang 2012
-
- Wang H, Tanaka Y, Kawauchi A, Miki T, Kayama Y, Koyama Y. Acupuncture of the sacral vertebrae suppresses bladder activity and bladder activity-related neurons in the brainstem micturition center. Neuroscience Research 2012;72(1):43-9. - PubMed
Ware 1992
-
- Ware JE, Sherbourne CD. The MOS 36-item short-form health survey (SF-36). I. Conceptual framework and item selection. Medical Care 1992;30(6):473-83. - PubMed
Wein 2009
-
- Wein AJ, Coyne KS, Tubaro A, Sexton CC, Kopp ZS, Aiyer LP. The impact of lower urinary tract symptoms on male sexual health: EpiLUTS. BJU International 2009;103(Suppl 3):33-41. - PubMed
White 2009
-
- White A, Editorial Board of Acupuncture in Medicine. Western medical acupuncture: a definition. Acupuncture in Medicine 2009;27(1):33-5. - PubMed
Witt 2009
-
- Witt CM, Pach D, Brinkhaus B, Wruck K, Tag B, Mank S, et al. Safety of acupuncture: results of a prospective observational study with 229,230 patients and introduction of a medical information and consent form. Forschende Komplementärmedizin 2009;16(2):91-7. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

