Endofungal Mycetohabitans rhizoxinica Bacteremia Associated with Rhizopus microsporus Respiratory Tract Infection
- PMID: 36148964
- PMCID: PMC9514336
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2810.220507
Endofungal Mycetohabitans rhizoxinica Bacteremia Associated with Rhizopus microsporus Respiratory Tract Infection
Abstract
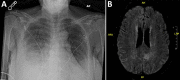
We report Mycetohabitans rhizoxinica bacteremia in a 65-year-old woman in California, USA, who was undergoing chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy for multiple myeloma. Acute brain infarction and pneumonia developed; Rhizopus microsporus mold was isolated from tracheal suction. Whole-genome sequencing confirmed bacteria in blood as genetically identical to endofungal bacteria inside the mold.
Keywords: Burkholderia rhizoxinica; Mycetohabitans rhizoxinica; Rhizopus microspores; United States; bacteremia; bacteria; endofungal bacteria; fungi; mucormycosis; respiratory infection.
Figures
References
-
- Estrada-de Los Santos P, Palmer M, Chávez-Ramírez B, Beukes C, Steenkamp ET, Briscoe L, et al. Whole genome analyses suggests that Burkholderia sensu lato contains two additional novel genera (Mycetohabitans gen. nov., and Trinickia gen. nov.): implications for the evolution of diazotrophy and nodulation in the Burkholderiaceae. Genes (Basel). 2018;9:389. 10.3390/genes9080389 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

