Exploring the roles of FGF/MAPK and cVG1/GDF signalling on mesendoderm induction and convergent extension during chick primitive streak formation
- PMID: 36149507
- PMCID: PMC9691481
- DOI: 10.1007/s00427-022-00696-1
Exploring the roles of FGF/MAPK and cVG1/GDF signalling on mesendoderm induction and convergent extension during chick primitive streak formation
Abstract
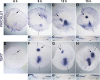
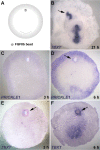
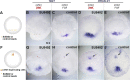
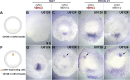
During primitive streak formation in the chick embryo, cells undergo mesendoderm specification and convergent extension at the same time and in the same cells. Previous work has implicated cVG1 (GDF3) as a key factor for induction of primitive streak identity and positioning the primitive streak, whereas FGF signalling was implicated in regulating cell intercalation via regulation of components of the WNT-planar cell polarity (PCP) pathway. FGF has also been reported to be able to induce a primitive streak (but lacking the most axial derivatives such as notochord/prechordal mesendoderm). These signals emanate from different cell populations in the embryo, so how do they interact to ensure that the same cells undergo both cell intercalation and acquire primitive streak identity? Here we begin to address this question by examining in more detail the ability of the two classes of signals in regulating the two developmental events. Using misexpression of inducers and/or exposure to inhibitors and in situ hybridisation, we study how these two signals regulate expression of Brachyury (TBXT) and PRICKLE1 as markers for the primitive streak and the PCP, respectively. We find that both signals can induce both properties, but while FGF seems to be required for induction of the streak by cVG1, it is not necessary for induction of PRICKLE1. The results are consistent with cVG1 being a common regulator for both primitive streak identity and the initiation of convergent extension that leads to streak elongation.
Keywords: Embryonic polarity; Epithelial cell intercalation; Gastrulation; Planar cell polarity; Primitive streak elongation.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The amniote primitive streak is defined by epithelial cell intercalation before gastrulation.Nature. 2007 Oct 25;449(7165):1049-52. doi: 10.1038/nature06211. Epub 2007 Oct 10. Nature. 2007. PMID: 17928866
-
FGF signalling through RAS/MAPK and PI3K pathways regulates cell movement and gene expression in the chicken primitive streak without affecting E-cadherin expression.BMC Dev Biol. 2011 Mar 21;11:20. doi: 10.1186/1471-213X-11-20. BMC Dev Biol. 2011. PMID: 21418646 Free PMC article.
-
Misexpression of chick Vg1 in the marginal zone induces primitive streak formation.Development. 1997 Dec;124(24):5127-38. doi: 10.1242/dev.124.24.5127. Development. 1997. PMID: 9362470
-
The mechanisms underlying primitive streak formation in the chick embryo.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2008;81:135-56. doi: 10.1016/S0070-2153(07)81004-0. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2008. PMID: 18023726 Review.
-
Induction and patterning of the primitive streak, an organizing center of gastrulation in the amniote.Dev Dyn. 2004 Mar;229(3):422-32. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.10458. Dev Dyn. 2004. PMID: 14991697 Review.
References
-
- Candia AF, Watabe T, Hawley SH, Onichtchouk D, Zhang Y, Derynck R, Niehrs C, Cho KW. Cellular interpretation of multiple TGF-beta signals: intracellular antagonism between activin/BVg1 and BMP-2/4 signaling mediated by Smads. Development. 1997;124:4467–4480. doi: 10.1242/dev.124.22.4467. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

