Interleukin 4/13 signaling in cardiac regeneration and repair
- PMID: 36149768
- PMCID: PMC9602781
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00310.2022
Interleukin 4/13 signaling in cardiac regeneration and repair
Abstract
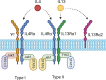
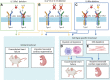
Interleukin 4 (IL4) and interleukin 13 (IL13) are closely related cytokines that have been classically attributed to type II immunity, namely, differentiation of T-helper 2 (TH2) cells and alternative activation of macrophages. Although the role of IL4/13 has been well described in various contexts such as defense against helminth parasites, pathogenesis of allergic disease, and several models of wound healing, relatively little is known about the role of IL4/13 in the heart following injury. Emerging literature has identified various roles for IL4/13 in animal models of cardiac regeneration as well as in the adult mammalian heart following myocardial injury. Notably, although IL4 and IL13 signal to hematopoietic cell types following myocardial infarction (MI) to promote wound healing phenotypes, there is substantial evidence that these cytokines can signal directly to non-hematopoietic cell types in the heart during development, homeostasis, and following injury. Comprehensive understanding of the molecular and cellular actions of IL4/13 in the heart is still lacking, but overall evidence to date suggests that activation of these cytokines results in beneficial outcomes with respect to cardiac repair. Here, we aim to comprehensively review the role of IL4 and IL13 and their prospective mechanisms in cardiac regeneration and repair.
Keywords: interleukin; myocardial infarction; regeneration.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chromatin landscape dynamics of the Il4-Il13 locus during T helper 1 and 2 development.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Aug 3;101(31):11410-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0403334101. Epub 2004 Jul 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15272080 Free PMC article.
-
Functional dissection identifies a conserved noncoding sequence-1 core that mediates IL13 and IL4 transcriptional enhancement.J Biol Chem. 2007 Feb 9;282(6):3738-46. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M606615200. Epub 2006 Dec 13. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17166845
-
Harnessing the Benefits of Neuroinflammation: Generation of Macrophages/Microglia with Prominent Remyelinating Properties.J Neurosci. 2021 Apr 14;41(15):3366-3385. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1948-20.2021. Epub 2021 Mar 12. J Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33712513 Free PMC article.
-
STAT6: its role in interleukin 4-mediated biological functions.J Mol Med (Berl). 1997 May;75(5):317-26. doi: 10.1007/s001090050117. J Mol Med (Berl). 1997. PMID: 9181473 Review.
-
Regulation of Th2 differentiation and Il4 locus accessibility.Annu Rev Immunol. 2006;24:607-56. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.23.021704.115821. Annu Rev Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16551261 Review.
Cited by
-
Polarized macrophages modulate cardiac structure and contractility under hypoxia in novel immuno-heart on a chip.APL Bioeng. 2025 May 1;9(2):026114. doi: 10.1063/5.0253888. eCollection 2025 Jun. APL Bioeng. 2025. PMID: 40322069 Free PMC article.
-
IL-4 and IL-13 in Cardiovascular Disease: From Immune Modulation to Therapeutic Possibilities - A Narrative Review.J Inflamm Res. 2025 Aug 8;18:10669-10679. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S531346. eCollection 2025. J Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 40809465 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Anti-Inflammatory COPD Treatments: Potential Cardiovascular Impacts.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2024 Nov 21;19:2481-2495. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S498255. eCollection 2024. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2024. PMID: 39606712 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Influence of Comorbidities on Chemokine and Cytokine Profile in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Patients: Preliminary Results.J Clin Med. 2023 Jan 19;12(3):801. doi: 10.3390/jcm12030801. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36769452 Free PMC article.
-
IL-13 promotes functional recovery after myocardial infarction via direct signaling to macrophages.JCI Insight. 2024 Jan 23;9(2):e172702. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.172702. JCI Insight. 2024. PMID: 38051583 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

